CD36 and Its Role in Regulating the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 36354702
- PMCID: PMC9688853
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29110642
CD36 and Its Role in Regulating the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
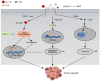
CD36 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that binds to a wide range of ligands, including fatty acids (FAs), cholesterol, thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) and thrombospondin-2 (TSP-2), and plays an important role in lipid metabolism, immune response, and angiogenesis. Recent studies have highlighted the role of CD36 in mediating lipid uptake by tumor-associated immune cells and in promoting tumor cell progression. In cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), CD36 regulates lipid uptake and matrix protein production to promote tumor proliferation. In addition, CD36 can promote tumor cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and induce epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT). In terms of tumor angiogenesis, CD36 binding to TSP-1 and TSP-2 can both inhibit tumor angiogenesis and promote tumor migration and invasion. CD36 can promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular mimicry (VM). Overall, we found that CD36 exhibits diverse functions in tumors. Here, we summarize the recent research findings highlighting the novel roles of CD36 in the context of tumors.
Keywords: CD36; angiogenesis; lipid metabolism; tumor-associated immune cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD36 promotes vasculogenic mimicry in melanoma by mediating adhesion to the extracellular matrix.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jul 2;21(1):765. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08482-4. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34215227 Free PMC article.
-
CD36-TSP-HRGP interactions in the regulation of angiogenesis.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(35):3559-67. doi: 10.2174/138161207782794185. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 18220792 Review.
-
Fatty Acids, CD36, Thrombospondin-1, and CD47 in Glioblastoma: Together and/or Separately?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):604. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020604. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD36-mediated activation of endothelial cell apoptosis by an N-terminal recombinant fragment of thrombospondin-2 inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis in vivo.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Jul;128(2):337-46. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1085-7. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 20714802 Free PMC article.
-
Context dependent role of the CD36--thrombospondin--histidine-rich glycoprotein axis in tumor angiogenesis and growth.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040033. Epub 2012 Jul 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22808089 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The molecular mechanism of thrombospondin family members in cardiovascular diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Mar 7;11:1337586. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1337586. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38516004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
scSDNE: A semi-supervised method for inferring cell-cell interactions based on graph embedding.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 May 7;21(5):e1013027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1013027. eCollection 2025 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40333631 Free PMC article.
-
Human CD36: Gene Regulation, Protein Function, and Its Role in Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;16(6):705. doi: 10.3390/genes16060705. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic crossroads: unravelling immune cell dynamics in gastrointestinal cancer drug resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Feb 8;8:7. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.164. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40051496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasome-related gene signatures as prognostic biomarkers in osteosarcoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(9):e18286. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18286. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38742843 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

