Marine Sources of DHA-Rich Phospholipids with Anti-Alzheimer Effect
- PMID: 36354985
- PMCID: PMC9695993
- DOI: 10.3390/md20110662
Marine Sources of DHA-Rich Phospholipids with Anti-Alzheimer Effect
Abstract
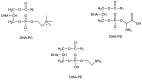
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex and progressive disease, which affects millions of people around the world. Despite the many efforts over the years to find efficient therapeutics, there is no cure yet. Nonetheless, many compounds have been proven to decrease Alzheimer's symptoms. After a short overview of the hypotheses considered in AD drug development and the drugs approved for AD treatment, which lead to symptom release, we focus on the valorization of natural marine sources that decrease AD symptoms, particularly on docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an important component in membrane phospholipids and the most abundant n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) found in gray matter of the brain and in retina and on the DHA-containing phospholipids (DHA-PLs) present in marine sources, namely fish, krill, mollusks and in fisheries and aquaculture by-products. DHA-PLs' bioactivities are presented, namely their properties in anti-neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, as anticancer agents, as well as their benefits to obesity and visual problems. Fisheries and aquaculture by-products are also highlighted as they have a high content of DHA and DHA-rich phospholipids, can be extracted by green methodologies and should be considered in a circular economy for a healthy sustainable future.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; docosahexaenoic acid; marine sources; phospholipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gordon R., Woodruff T.M. Neuroinflammation as a Therapeutic Target in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

