LC-HRMS Profiling of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Mytilus galloprovincialis after a Gymnodinium catenatum Bloom
- PMID: 36355003
- PMCID: PMC9694030
- DOI: 10.3390/md20110680
LC-HRMS Profiling of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Mytilus galloprovincialis after a Gymnodinium catenatum Bloom
Abstract
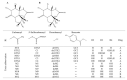
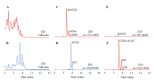
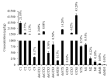
Saxitoxin and its more than 50 analogues are a group of naturally occurring neurotoxins collectively designated as paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs). PSTs are toxic to humans and maximum legal limits in seafood have been implemented by regulatory authorities worldwide. In the European Union, monitoring of PSTs is performed using the AOAC Official Method 2005.06, based on liquid chromatography coupled with fluorescence detection (LC- FLD). However, this method has been suggested to not effectively detect the emerging C-11 hydroxyl (M-toxins) and benzoate (GC-toxins) analogues, with these analogues currently not being surveyed in monitoring programs. In this study, a liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) method was used to search for these emerging PSTs in mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis, contaminated following an intense Gymnodinium catenatum bloom in the Tagus estuary (Lisbon, Portugal). Five M-toxins (M1, M2, M6, dcM6, and dcM10), but no GC-toxins, were detected in the mussels' whole-soft body tissue. Moreover, the classical PSTs (C1 to C4, GTX 4 to GTX6, dcGTX1 to dcGTX4, dcSTX, dcNEO, and STX) were also found and comprised the largest fraction of the PSTs' profile. The presence of unregulated PSTs in edible mussel samples suggests potential seafood safety risks and urges further research to determine the frequency of these analogues in seafood and their contribution to toxicity.
Keywords: European waters; GC-toxins; Gymnodinium catenatum; LC-HRMS; M-toxins; emergent toxins; marine biotoxins; occurrence data; seafood safety; shellfish poisoning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shumway S.E. Phycotoxin-related shellfish poisoning: Bivalve molluscs are not the only vectors. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1995;3:1–31. doi: 10.1080/10641269509388565. - DOI
-
- Bricelj V.M., Shumway S.E. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs: Occurrence, Transfer Kinetics, and Biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998;6:315–383. doi: 10.1080/10641269891314294. - DOI
-
- FAO . Food and Nutrition Paper 80. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2004.
-
- Standard for Live and Raw Bivalve Molluscs. Codex Alimentarius Commission; Rome, Italy: 2008. p. 292.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 101003376/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodow-ska-Curie Widening Fellowship
- UIDB/04326/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- UIDP/04326/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- LA/P/0101/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- EMBRC.PT ALG-01-0145-FEDER-022121/CRESC Algarve 2020 and COMPETE 2020
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

