Complexing the Marine Sesquiterpene Euplotin C by Means of Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges: A Preliminary Investigation
- PMID: 36355005
- PMCID: PMC9692710
- DOI: 10.3390/md20110682
Complexing the Marine Sesquiterpene Euplotin C by Means of Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges: A Preliminary Investigation
Abstract
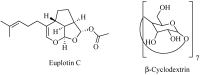
Euplotin C is a sesquiterpene of marine origin endowed with significant anti-microbial and anti-tumor properties. Despite the promising functional profile, its progress as a novel drug candidate has failed so far, due to its scarce solubility and poor stability in aqueous media, such as biological fluids. Therefore, overcoming these limits is an intriguing challenge for the scientific community. In this work, we synthesized β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges and investigated their use as colloidal carriers for stably complex euplotin C. Results obtained proved the ability of the carrier to include the natural compound, showing remarkable values of both loading efficiency and capacity. Moreover, it also allowed us to preserve the chemical structure of the loaded compound, which was recovered unaltered once extracted from the complex. Therefore, the use of β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges represents a viable option to vehiculate euplotin C, thus opening up its possible use as pharmacologically active compound.
Keywords: ATR-FTIR analysis; ESI-MS analysis; LC-DAD-ESI-MS analysis; NMR analysis; SPE; euplotin C; β-cyclodextrin; β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Trielli F., Cervia D., Di Giuseppe G., Ristori C., Kruppel T., Burlando B., Guella G., Viarengo A., Bagnoli P., Umberta M., et al. Action mechanisms of the secondary metabolite euplotin C: Signaling and functional role in Euplotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2008;55:365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2008.00335.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cervia D., Martini D., Garcia-Gil M., Di Giuseppe G., Guella G., Dini F., Bagnoli P. Cytotoxic effects and apoptotic signalling mechanisms of the sesquiterpenoid euplotin C, a secondary metabolite of the marine ciliate Euplotes crassus, in tumour cells. Apoptosis. 2006;11:829–843. doi: 10.1007/s10495-006-5700-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

