Rhizophora mucronata Lam. (Mangrove) Bark Extract Reduces Ethanol-Induced Liver Cell Death and Oxidative Stress in Swiss Albino Mice: In Vivo and In Silico Studies
- PMID: 36355104
- PMCID: PMC9698744
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12111021
Rhizophora mucronata Lam. (Mangrove) Bark Extract Reduces Ethanol-Induced Liver Cell Death and Oxidative Stress in Swiss Albino Mice: In Vivo and In Silico Studies
Abstract
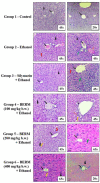
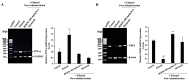
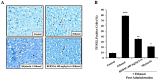
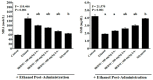
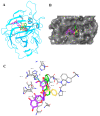
The bark extract of Rhizophora mucronata (BERM) was recently reported for its prominent in vitro protective effects against liver cell line toxicity caused by various toxicants, including ethanol. Here, we aimed to verify the in vivo hepatoprotective effects of BERM against ethanol intoxication with the prediction of potential targets employing in silico studies. An oral administration of different concentrations (100, 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight) of BERM before high-dose ethanol via intraperitoneal injection was performed in mice. On day 7, liver sections were dissected for histopathological examination. The ethanol intoxication caused liver injury and large areas of necrosis. The pre-BERM administration decreased the ethanol-induced liver damage marker tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) expression, reduced hepatotoxicity revealed by nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragmentation and decreased oxidative stress indicated by malondialdehyde and glutathione contents. Our in silico studies have identified BERM-derived metabolites exhibiting the highest predicted antioxidant and free radical scavenger activities. Molecular docking studies showed that most of the metabolites were predicted to be enzyme inhibitors such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, which were reported to stimulate the antioxidant defense system. The metabolites predominantly presented acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety profiles, suggesting them as promising new antioxidant agents. Altogether, the BERM extract exerts antioxidative activities and shows promising hepatoprotective effects against ethanol intoxication. Identification of related bioactive compounds will be of interest for future use at physiological concentrations in ethanol-intoxicated individuals.
Keywords: Rhizophora mucronata; ethanol intoxication; hepatoprotection; liver injury; metabolites; necrosis; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HPLC characterization, acute and sub-acute toxicity evaluation of bark extract of Rhizophora mucronata in Swiss Albino mice.Heliyon. 2019 Dec 31;6(1):e03108. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03108. eCollection 2020 Jan. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31909272 Free PMC article.
-
Propugnating Effect of Bark of Rhizophora mucronata Against Different Toxicants Viz Carbon Tetrachloride, Ethanol and Paracetamol on HepG2 Cell Lines.J Pharmacopuncture. 2019 Mar;22(1):41-48. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2019.22.005. Epub 2019 Mar 31. J Pharmacopuncture. 2019. PMID: 30989000 Free PMC article.
-
The Potency of Red Seaweed (Eucheuma cottonii) Extracts as Hepatoprotector on Lead Acetate-induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Jul-Sep;9(3):282-286. doi: 10.4103/pr.pr_69_16. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 28827971 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of the ethanol extract of Vitis thunbergii on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats through anti-oxidative activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Aug 1;142(3):795-803. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Jun 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22698911
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-adherent effects of Rhizophora apiculata bark and leaf extracts and computational prediction of the effects of its compound on β-tubulin interaction in Acanthamoeba triangularis genotype 4.Vet World. 2024 Dec;17(12):2829-2845. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.2829-2845. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 39897349 Free PMC article.
-
Boswellia carteri Birdw. Resin Extract Induces Phase-I Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme Gene Expressions in Human Hepatocarcinoma (Hep G2) Cells: In vitro and in silico Studies.Biologics. 2025 May 5;19:289-320. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S491278. eCollection 2025. Biologics. 2025. PMID: 40352903 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review on anti-inflammatory plants: a mechanistic insight through preclinical and clinical studies.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May;33(5):2447-2476. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01764-4. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40465037 Review.
References
-
- Arab J.P., Roblero J.P., Altamirano J., Bessone F., Araujo R.C., la Tijera F.H.-D., Restrepo-Gutiérrez J.C., Torre A., Urzua A., Simonetto D.A., et al. Alcohol-related liver disease: Clinical practice guidelines by the Latin American Association for the Study of the Liver (ALEH) Ann. Hepatol. 2019;18:518–535. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2019.04.005. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

