Urine Metabolites Enable Fast Detection of COVID-19 Using Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 36355139
- PMCID: PMC9697918
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12111056
Urine Metabolites Enable Fast Detection of COVID-19 Using Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
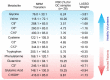
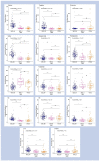
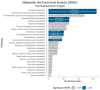
The COVID-19 pandemic boosted the development of diagnostic tests to meet patient needs and provide accurate, sensitive, and fast disease detection. Despite rapid advancements, limitations related to turnaround time, varying performance metrics due to different sampling sites, illness duration, co-infections, and the need for particular reagents still exist. As an alternative diagnostic test, we present urine analysis through flow-injection-tandem mass spectrometry (FIA-MS/MS) as a powerful approach for COVID-19 diagnosis, targeting the detection of amino acids and acylcarnitines. We adapted a method that is widely used for newborn screening tests on dried blood for urine samples in order to detect metabolites related to COVID-19 infection. We analyzed samples from 246 volunteers with diagnostic confirmation via PCR. Urine samples were self-collected, diluted, and analyzed with a run time of 4 min. A Lasso statistical classifier was built using 75/25% data for training/validation sets and achieved high diagnostic performances: 97/90% sensitivity, 95/100% specificity, and 95/97.2% accuracy. Additionally, we predicted on two withheld sets composed of suspected hospitalized/symptomatic COVID-19-PCR negative patients and patients out of the optimal time-frame collection for PCR diagnosis, with promising results. Altogether, we show that the benchmarked FIA-MS/MS method is promising for COVID-19 screening and diagnosis, and is also potentially useful after the peak viral load has passed.
Keywords: COVID-19; amino acids; diagnostic; metabolomics; urine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pritt B.S., Wang P., Nuzzo J., Zimmermann S., Burnham C.-A.D. Deadly Pathogens, Transformative Technologies, and Protracted Pandemics: Challenges and Opportunities in Laboratory Medicine. Clin. Chem. 2022;68:1–3. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvab244. - DOI
-
- Fernandes Q., Inchakalody V.P., Merhi M., Mestiri S., Taib N., Moustafa Abo El-Ella D., Bedhiafi T., Raza A., Al-Zaidan L., Mohsen M.O., et al. Emerging COVID-19 variants and their impact on SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, therapeutics and vaccines. Ann. Med. 2022;54:524–540. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2031274. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lima N.M., Fernandes B.L.M., Alves G.F., de Souza J.C.Q., Siqueira M.M., Patrícia do Nascimento M., Moreira O.B.O., Sussulini A., de Oliveira M.A.L. Mass spectrometry applied to diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic targets identification for the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2022;1195:339385. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339385. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

