Plasma Metabolome Alterations Discriminate between COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Pneumonia
- PMID: 36355140
- PMCID: PMC9693035
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12111058
Plasma Metabolome Alterations Discriminate between COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Pneumonia
Abstract
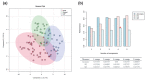
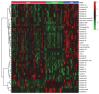
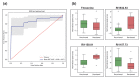
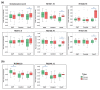
Pneumonia is a common cause of morbidity and mortality and is most often caused by bacterial pathogens. COVID-19 is characterized by lung infection with potential progressive organ failure. The systemic consequences of both disease on the systemic blood metabolome are not fully understood. The aim of this study was to compare the blood metabolome of both diseases and we hypothesize that plasma metabolomics may help to identify the systemic effects of these diseases. Therefore, we profiled the plasma metabolome of 43 cases of COVID-19 pneumonia, 23 cases of non-COVID-19 pneumonia, and 26 controls using a non-targeted approach. Metabolic alterations differentiating the three groups were detected, with specific metabolic changes distinguishing the two types of pneumonia groups. A comparison of venous and arterial blood plasma samples from the same subjects revealed the distinct metabolic effects of pulmonary pneumonia. In addition, a machine learning signature of four metabolites was predictive of the disease outcome of COVID-19 subjects with an area under the curve (AUC) of 86 ± 10 %. Overall, the results of this study uncover systemic metabolic changes that could be linked to the etiology of COVID-19 pneumonia and non-COVID-19 pneumonia.
Keywords: COVID-19; community-acquired pneumonia; machine learning; mass spectrometry; metabolic profiling; metabolomics; multivariate statistics; non-COVID-19 pneumonia; plasma; system biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chowdhury S.D., Oommen A.M. Epidemiology of COVID-19. J. Dig. Endosc. 2020;11:3. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1712187. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

