Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-A Concise Review of Noninvasive Tests and Biomarkers
- PMID: 36355154
- PMCID: PMC9692389
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12111073
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-A Concise Review of Noninvasive Tests and Biomarkers
Abstract
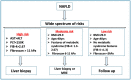
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease worldwide, with a continuously growing prevalence. The pathophysiology of the disease is complex and includes several mechanisms, with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance playing a major role. It is crucial to diagnose NAFLD before it advances to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to cirrhosis, presented by its complications which include ascites, portal hypertension, bleeding varices and encephalopathy. Another important complication of NAFLD and cirrhosis is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a cancer with increasing incidence and poor prognosis. Even with the growing prevalence of NAFLD, diagnosis via liver biopsies is unrealistic, considering the costs and complications. Noninvasive tests, including serum biomarkers and elastography, are cost-effective and convenient, thereby replacing liver biopsies in diagnosing and excluding liver fibrosis. However, currently, these noninvasive tests have several limitations, such as variability, inadequate accuracy and risk factors for error. The limitations and variability of these tests comet the investigator to propose combining them in diagnostic algorithms to produce more accurate tools. Identifying patients with significant fibrosis is important for targeted therapies to prevent disease progression. Effective screening using noninvasive tests can be crucial for patient risk stratification and early diagnosis.
Keywords: Keywords: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); advanced fibrosis; biomarkers; liver cancer; metabolic syndrome; metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD); non-invasive test (NIT); nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- McGlinchey A.J., Govaere O., Geng D., Ratziu V., Allison M., Bousier J., Petta S., de Oliviera C., Bugianesi E., Schattenberg J.M., et al. Metabolic signatures across the full spectrum of non- alcoholic fatty liver disease. JHEP Rep. 2022;4:100477. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100477. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources