TMEM196 inhibits lung cancer metastasis by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- PMID: 36355209
- PMCID: PMC11797904
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04363-w
TMEM196 inhibits lung cancer metastasis by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Abstract
Purpose: The TMEM196 protein, which comprises four membrane-spanning domains, belongs to the TMEM protein family. TMEM196 was identified as a candidate tumor suppressor gene in lung cancer. However, its role and mechanism in lung cancer metastasis remain unclear. Here, we study the role of TMEM196 in tumor metastasis to further verify the function in lung cancer.
Methods: In this study, we used qRT-PCR, western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry to examine the expression levels of TMEM196 and related proteins in lung cancer tissues and tumor cells. We utilized Transwell assays, xenograft nude mouse models, and TMEM196-/- mouse models to evaluate the effects of TMEM196 on tumor invasion and metastasis. Finally, we used bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase reporter gene assays to explore the molecular mechanism of TMEM196 as a tumor suppressor.
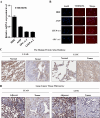
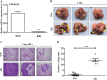
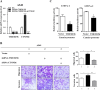
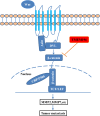
Results: We found that TMEM196 mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly decreased in lung cancer tissues and cells. Low expression of TMEM196 in clinical patients was associated with poor prognosis. TMEM196 strongly inhibited tumor metastasis and progression in vitro and in vivo. The primary lung tumors induced by tail vein-inoculated B16 cells in TMEM196-/- mice were significantly larger than those in TMEM196+/+ mice. Mechanistically, TMEM196 inhibited the Wnt signaling pathway and repressed β-catenin promoter transcription. TMEM196 silencing in lung cancer cells and mice resulted in significant upregulation of the expression of β-catenin and Wnt signaling pathway downstream target genes (MMP2 and MMP7). Decreasing β-catenin expression in TMEM196-silenced cancer cells attenuated the antimetastatic effect of TMEM196.
Conclusions: Our results revealed that TMEM196 acts as a novel lung cancer metastasis suppressor via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: Lung cancer; Metastasis; TMEM196; Tumor suppressor; Wnt signaling.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
DSG3 promotes bladder cancer growth and metastasis via AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 2;23(1):729. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06754-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40605005 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-related CMTM6 promotes glioblastoma progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway and acts as an onco-immunological biomarker.J Gene Med. 2024 May;26(5):e3685. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3685. J Gene Med. 2024. PMID: 38686653
-
CST2 promotes cell proliferation and regulates cell cycle by activating Wnt-β-catenin signalling pathway in serous ovarian cancer.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2024 Dec;44(1):2363515. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2024.2363515. Epub 2024 Jun 12. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2024. PMID: 38864487
-
Role of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in cancer drug resistance: Insights into molecular aspects of major solid tumors.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Oct 15;729:150348. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150348. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38986260 Review.
-
Experimental toolkit to study the oncogenic role of WNT signaling in colorectal cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025 Sep;1880(4):189354. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2025.189354. Epub 2025 May 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40414319 Review.
Cited by
-
[TMEM64 is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor cell proliferation and invasion].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Aug 20;43(8):1345-1355. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.08.11. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37712271 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The roles and functions of TMEM protein family members in cancers, cardiovascular and kidney diseases (Review).Biomed Rep. 2025 Feb 11;22(4):63. doi: 10.3892/br.2025.1941. eCollection 2025 Apr. Biomed Rep. 2025. PMID: 39991002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of transmembrane proteins in tumorigenesis and therapy.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):1447-1466. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1660. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40104699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-1246 enhances chemo-resistance of polyploid giant cancer cells in H1299 cells by targeting GSK3β/β-catenin.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 24;16(1):901. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02756-0. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40411667 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the development and therapeutic resistance of non-small cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 13;22(1):565. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05380-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38872189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berglund E, Akcakaya P, Berglund D et al (2014) Functional role of the Ca2+-activated Cl- channel DOG1/TMEM16A in gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells. Exp Cell Res 326(2):315–325. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.05.003 - PubMed
-
- Blomme A, Costanza B, De TP et al (2017) Myoferlin regulates cellular lipid metabolism and promotes metastases in triplenegative breast cancer. Oncogene 36(15):2116–2130. 10.1038/onc.2016.369 - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA-Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

