Cost-effectiveness of Prostate Cancer Screening Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging or Standard Biopsy Based on the STHLM3-MRI Study
- PMID: 36355382
- PMCID: PMC9650623
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.5252
Cost-effectiveness of Prostate Cancer Screening Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging or Standard Biopsy Based on the STHLM3-MRI Study
Abstract
Importance: The combination of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for prostate cancer detection has rarely been evaluated in a screening context. The STHLM3-MRI screening-by-invitation study (NCT03377881) has reported the benefits of using MRI with subsequent combined targeted and standard biopsies compared with using standard biopsies alone.
Objective: To investigate the cost-effectiveness of prostate cancer screening using MRI with combined targeted and standard biopsies compared with standard biopsies alone among men aged 55 to 69 years in Sweden, based on evidence from the STHLM3-MRI study.
Design, setting, and participants: This economic evaluation study was conducted from a lifetime health care perspective using a microsimulation model to evaluate no screening and screening strategies among adult men in Sweden. Men aged 55 to 69 years in Sweden were simulated for no screening and screening strategies. Input parameters were obtained from the STHLM3-MRI study and recent reviews. One-way and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were performed in May 2022.
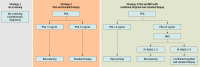
Interventions: No screening, quadrennial PSA screening using standard biopsies alone, and MRI-based screening using combined targeted and standard biopsies.
Main outcomes and measures: The number of tests, incidence, deaths, costs, quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were estimated.
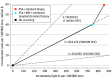
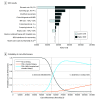
Results: A total 603 men were randomized to the standard arm, 165 of these participants (27.4%) did not undergo standard biopsy; 929 men were randomized to the experimental arm, 111 (11.9%) of whom did undergo MRI or any biopsy. Compared with no screening, the screening strategies were associated with reduced lifetime prostate cancer-related deaths by 6% to 9%. Screening with MRI and the combined biopsies resulted in an ICER of US $53 736, which is classified as a moderate cost per QALY gained in Sweden. Relative to screening with standard biopsies alone, MRI-based screening reduced the number of both lifetime biopsies and overdiagnosis by approximately 50% and had a high probability of being cost-effective than the traditional PSA screening.
Conclusions and relevance: For prostate cancer screening, this economic evaluation study found that PSA testing followed by MRI with subsequent combined targeted and standard biopsies had a high probability to be more cost-effective compared with the traditional screening pathway using PSA and standard biopsy. MRI-based screening may be considered for early detection of prostate cancer in Sweden.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Beyond the AJR: Biparametric MRI-Based Prostate Cancer Screening-A Cost-Effective Alternative to PSA Screening and Standard Biopsy.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2023 Sep;221(3):389. doi: 10.2214/AJR.23.29011. Epub 2023 Jan 18. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2023. PMID: 36651610 No abstract available.
-
Prostate-Specific Antigen Screening Should Not Be Covered by Publicly Funded Health Insurance.JAMA Oncol. 2023 Jun 1;9(6):867-868. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.0254. JAMA Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37052905 No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

