Identification of a Novel p53 Modulator Endowed with Antitumoural and Antibacterial Activity through a Scaffold Repurposing Approach
- PMID: 36355491
- PMCID: PMC9692514
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15111318
Identification of a Novel p53 Modulator Endowed with Antitumoural and Antibacterial Activity through a Scaffold Repurposing Approach
Abstract
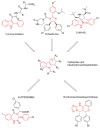
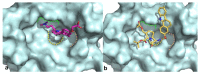
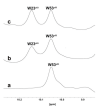
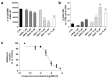
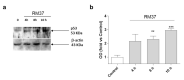
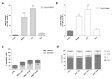
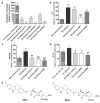
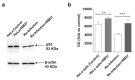
Intracellular pathogens, such as Chlamydia trachomatis, have been recently shown to induce degradation of p53 during infection, thus impairing the protective response of the host cells. Therefore, p53 reactivation by disruption of the p53-MDM2 complex could reduce infection and restore pro-apoptotic effect of p53. Here, we report the identification of a novel MDM2 inhibitor with potential antitumoural and antibacterial activity able to reactivate p53. A virtual screening was performed on an in-house chemical library, previously synthesised for other targets, and led to the identification of a hit compound with a benzo[a]dihydrocarbazole structure, RM37. This compound induced p53 up-regulation in U343MG glioblastoma cells by blocking MDM2-p53 interaction and reduced tumour cell growth. NMR studies confirmed its ability to dissociate the MDM2-p53 complex. Notably, RM37 reduced Chlamydia infection in HeLa cells in a concentration-dependent manner and ameliorated the inflammatory status associated with infection.
Keywords: Chlamydia trachomatis; antibacterial activity; glioblastoma multiforme; p53 modulator; p53–MDM2 complex; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chlamydia infection depends on a functional MDM2-p53 axis.Nat Commun. 2014 Nov 13;5:5201. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6201. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25392082 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia trachomatis plasmid-encoded protein Pgp3 inhibits apoptosis via the PI3K-AKT-mediated MDM2-p53 axis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Feb;452(1-2):167-176. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3422-9. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30132214
-
Discovery of a new small-molecule inhibitor of p53-MDM2 interaction using a yeast-based approach.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 May 1;85(9):1234-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.01.032. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23428467
-
Medicinal Chemistry Strategies to Disrupt the p53-MDM2/MDMX Interaction.Med Res Rev. 2016 Sep;36(5):789-844. doi: 10.1002/med.21393. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Med Res Rev. 2016. PMID: 27302609 Review.
-
Therapeutic opportunities in cancer therapy: targeting the p53-MDM2/MDMX interactions.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 15;11(12):5762-5781. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35018225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repurposing of apoptotic inducer drugs against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 28;15(1):7109. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91096-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40016256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Purdie C., Harrison D., Peter A., Dobbie L., White S., Howie S., Salter D., Bird C., Wyllie A., Hooper M. Tumour Incidence, Spectrum and Ploidy in Mice with a Large Deletion in the P53 Gene. Oncogene. 1994;9:603–609. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

