The Therapeutic Potential of Plant Polysaccharides in Metabolic Diseases
- PMID: 36355500
- PMCID: PMC9695998
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15111329
The Therapeutic Potential of Plant Polysaccharides in Metabolic Diseases
Abstract
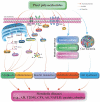
Plant polysaccharides (PPS) composed of more than 10 monosaccharides show high safety and various pharmacological activities, including immunoregulatory, antitumor, antioxidative, antiaging, and other effects. In recent years, emerging evidence has indicated that many PPS are beneficial for metabolic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, obesity, and neurological diseases, which are usually caused by the metabolic disorder of fat, sugar, and protein. In this review, we introduce the common characteristics and functional activity of many representative PPS, emphasize the common risks and molecular mechanism of metabolic diseases, and discuss the pharmacological activity and mechanism of action of representative PPS obtained from plants including Aloe vera, Angelica sinensis, pumpkin, Lycium barbarum, Ginseng, Schisandra chinensis, Dioscorea pposite, Poria cocos, and tea in metabolic diseases. Finally, this review will provide directions and a reference for future research and for the development of PPS into potential drugs for the treatment of metabolic diseases.
Keywords: characteristics; mechanism of action; metabolic disease; pharmacological activities; plant polysaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An evidence-based update on the pharmacological activities and possible molecular targets of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Dec 17;9:33-78. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S72892. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25552899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant activities of some common ingredients of traditional chinese medicine, Angelica sinensis, Lycium barbarum and Poria cocos.Phytother Res. 2004 Dec;18(12):1008-12. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1617. Phytother Res. 2004. PMID: 15742346
-
Poria cocos Polysaccharides Alleviates Chronic Nonbacterial Prostatitis by Preventing Oxidative Stress, Regulating Hormone Production, Modifying Gut Microbiota, and Remodeling the DNA Methylome.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Nov 11;68(45):12661-12670. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c05943. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 33119288
-
Effects of Polysaccharides in Lycium Barbarum Berries from Different Regions of China on Macrophages Function and their Correlation to the Glycosidic Linkages.J Food Sci. 2017 Oct;82(10):2411-2420. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13813. Epub 2017 Aug 23. J Food Sci. 2017. PMID: 28833151
-
Immune activities of polysaccharides isolated from Lycium barbarum L. What do we know so far?Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jan;229:107921. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107921. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34174277 Review.
Cited by
-
An analysis of the nutritional effects of Schisandra chinensis components based on mass spectrometry technology.Front Nutr. 2023 Jul 25;10:1227027. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1227027. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37560060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronidase Promote Transdermal Diffusion of Small Sized Curcumin Nanocrystal by Dissolving Microneedles Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 27;15(3):788. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030788. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986649 Free PMC article.
-
Forecasting cardiovascular disease mortality using artificial neural networks in Sindh, Pakistan.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 4;25(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21187-0. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39754102 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Global Physical Capacity Score in Key Parameters of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD).J Clin Med. 2025 May 29;14(11):3821. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113821. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507592 Free PMC article.
-
The Interaction Between Nutraceuticals and Gut Microbiota: a Novel Therapeutic Approach to Prevent and Treatment Parkinson's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):9078-9109. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04151-2. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38587699 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 81903829/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020YJ0494/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province
- SKL-QRCM(MUST)-2020-2022 and MUST-SKL-2021-005/Macao Science and Technology Development Fund of Macao SAR
- 2021ZKZD015, 2021ZKZD018, and 2021ZKMS046/Southwest Medical University
- 2020LZXNYDJ37/Joint of Luzhou Municipal People's Government and Southwest Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

