Composing On-Program Triggers and On-Demand Stimuli into Biosensor Drug Carriers in Drug Delivery Systems for Programmable Arthritis Therapy
- PMID: 36355502
- PMCID: PMC9698912
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15111330
Composing On-Program Triggers and On-Demand Stimuli into Biosensor Drug Carriers in Drug Delivery Systems for Programmable Arthritis Therapy
Abstract
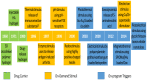
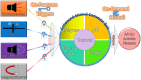
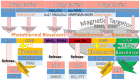
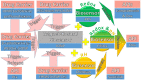
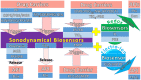
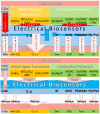
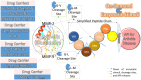
Medication in arthritis therapies is complex because the inflammatory progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) is intertwined and influenced by one another. To address this problem, drug delivery systems (DDS) are composed of four independent exogenous triggers and four dependent endogenous stimuli that are controlled on program and induced on demand, respectively. However, the relationships between the mechanisms of endogenous stimuli and exogenous triggers with pathological alterations remain unclear, which results in a major obstacle in terms of clinical translation. Thus, the rationale for designing a guidance system for these mechanisms via their key irritant biosensors is in high demand. Many approaches have been applied, although successful clinical translations are still rare. Through this review, the status quo in historical development is highlighted in order to discuss the unsolved clinical difficulties such as infiltration, efficacy, drug clearance, and target localisation. Herein, we summarise and discuss the rational compositions of exogenous triggers and endogenous stimuli for programmable therapy. This advanced active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) implanted dose allows for several releases by remote controls for endogenous stimuli during lesion infections. This solves the multiple implantation and local toxic accumulation problems by using these flexible desired releases at the specified sites for arthritis therapies.
Keywords: biosensors; drug carriers; drug delivery systems; endogenous stimuli; exogenous triggers; pathological alterations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stimuli-responsive Drug Delivery Systems as an Emerging Platform for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(2):155-165. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190321104424. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 30907308 Review.
-
Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Feb 21;14:100223. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100223. eCollection 2022 Mar. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35243298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review of advanced drug delivery systems for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Pharm. 2023 Mar 25;635:122698. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122698. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36754181 Review.
-
Endogenous and Exogenous Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems for Programmed Site-Specific Release.Molecules. 2019 Mar 21;24(6):1117. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061117. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30901827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CuZn Complex Used in Electrical Biosensors for Drug Delivery Systems.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 1;15(21):7672. doi: 10.3390/ma15217672. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36363264 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Microbial siderophores as molecular shuttles for metal cations: sources, sinks and application perspectives.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Aug 29;205(9):322. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03644-3. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37644212 Review.
-
Effect of Porosity and Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Additive Manufactured CoCrMo Alloys.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;16(2):751. doi: 10.3390/ma16020751. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676489 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Copper and Zinc into a Biosensor for Anti-Chemoresistance and Achieving Osteosarcoma Therapeutic Efficacy.Molecules. 2023 Mar 24;28(7):2920. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072920. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclodextrins as multifunctional tools for advanced biomaterials in tissue repair and regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2025 Mar 27;49:627-651. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.03.018. eCollection 2025 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40212783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of ketorolac for postoperative pain management in lumbar spine surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 5;13(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02685-z. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39501393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michallek F., Ulas S.T., Poddubnyy D., Proft F., Schneider U., Hermann K.-G.A., Dewey M., Diekhoff T. Fractal analysis of perfusion imaging in synovitis: A novel imaging biomarker for grading inflammatory activity based on assessing angiogenesis. RMD Open. 2022;8:e002078. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002078. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

