Combined Effects of Methyldopa and Baicalein or Scutellaria baicalensis Roots Extract on Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, and Expression of Inflammatory and Vascular Disease-Related Factors in Spontaneously Hypertensive Pregnant Rats
- PMID: 36355514
- PMCID: PMC9694684
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15111342
Combined Effects of Methyldopa and Baicalein or Scutellaria baicalensis Roots Extract on Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, and Expression of Inflammatory and Vascular Disease-Related Factors in Spontaneously Hypertensive Pregnant Rats
Abstract
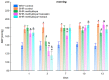
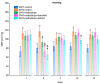
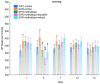
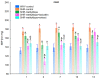
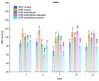
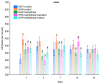
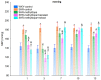
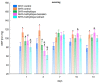
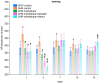
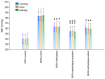
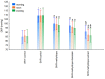
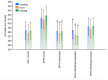
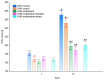
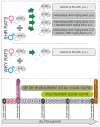
The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of baicalein or Scutellaria baicalensis root extract interaction with methyldopa in pregnant spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) at the pharmacodynamic, molecular, and biochemical levels. The rats, after confirming pregnancy, received baicalein (200 mg/kg/day, p.o.) and extract (1000 mg/kg/day, p.o.), in combination with methyldopa (400 mg/kg/day; p.o.), for 14 consecutive days, 1 h before blood pressure and heart rate measurements. In the heart and placenta from mothers after giving birth to their offspring, mRNA expression of factors related to inflammatory processes (TNF-α, Il-1β, IL-6) and vascular diseases (TGF-β, HIF-1α, VEGF, PlGF) was measured. Levels of markers of oxidative stress (superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde) in the placenta and indicators of myocardial damage (troponin cTnC and cTnI, creatine kinase, myoglobin, and lactate dehydrogenase) in the heart were also assessed. Baicalein co-administered with methyldopa was associated with reduced blood pressure, especially during the first three days. The interactions were more pronounced for such factors as TGF-β, HIF-1α, VEGF, and PlGF than TNF-α, Il-1β, and IL-6. Combined application of baicalein and extract with methyldopa may be of value in the development of a new antihypertensive medication intended for patients suffering from preeclampsia or pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Keywords: Scutellaria baicalensis; baicalein; blood pressure; inflammatory and vascular factors; mRNA expression; methyldopa; oxidative stress; placenta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined Effects of Methyldopa and Flavonoids on the Expression of Selected Factors Related to Inflammatory Processes and Vascular Diseases in Human Placenta Cells-An In Vitro Study.Molecules. 2021 Feb 26;26(5):1259. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051259. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33652665 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of baicalein and wogonin isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis roots on skin damage in acute UVB-irradiated hairless mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Jul 1;661(1-3):124-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.04.033. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21549115
-
Baicalein protects isoproterenol induced myocardial ischemic injury in male Wistar rats by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation.Inflamm Res. 2016 Aug;65(8):613-22. doi: 10.1007/s00011-016-0944-z. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Inflamm Res. 2016. PMID: 27071824
-
Biological properties of baicalein in cardiovascular system.Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2005 Apr;5(2):177-84. doi: 10.2174/1568006043586206. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2005. PMID: 15853750 Review.
-
Baicalein: promising therapeutic applications with special reference to published patents.Pharm Pat Anal. 2022 Jan;11(1):23-32. doi: 10.4155/ppa-2021-0027. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Pharm Pat Anal. 2022. PMID: 35345898 Review.
Cited by
-
Baicalin Mitigates Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis by Inhibiting the p85a Subunit of PI3K.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 19;13(1):232. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010232. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857815 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-related biomarkers in preeclampsia: the underlying mechanism, correlation to the immune microenvironment and drug screening.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06211-2. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38166707 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

