Vasorelaxant Effects of Syzygium samarangense (Blume) Merr. and L.M.Perry Extract Are Mediated by NO/cGMP Pathway in Isolated Rat Thoracic Aorta
- PMID: 36355521
- PMCID: PMC9692616
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15111349
Vasorelaxant Effects of Syzygium samarangense (Blume) Merr. and L.M.Perry Extract Are Mediated by NO/cGMP Pathway in Isolated Rat Thoracic Aorta
Abstract
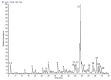
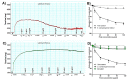
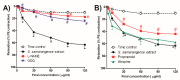
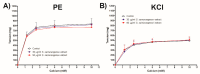
Syzygium samarangense (Blume) Merr. and L.M.Perry is utilized widely in traditional medicine. We have reported previously a wide array of pharmacological properties of its leaf extract, among them anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, antiulcer, and antitrypanosomal activities. We also annotated its chemical composition using LC-MS/MS. Here, we continue our investigations and evaluate the vasorelaxant effects of the leaf extract on aortic rings isolated from rats and explore the possible underlying mechanisms. S. samarangense extract induced a concentration dependent relaxation of the phenylephrine-precontracted aorta in the rat model. However, this effect disappeared upon removing the functional endothelium. Pretreating the aortic tissues either with propranolol or NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester inhibited the relaxation induced by the extract; however, atropine did not affect the extract-induced vasodilation. Meanwhile, adenylate cyclase inhibitor, MDL; specific guanylate cyclase inhibitor, ODQ; high extracellular KCl; and indomethacin as cyclooxygenase inhibitor inhibited the extract-induced vasodilation. On the other hand, incubation of S. samarangense extract with aortae sections having their intact endothelium pre-constricted using phenylephrine or KCl in media free of Ca2+ showed no effect on the constriction of the aortae vessels induced by Ca2+. Taken together, the present study suggests that S. samarangense extract dilates isolated aortic rings via endothelium-dependent nitric oxide (NO)/cGMP signaling. The observed biological effects could be attributed to its rich secondary metabolites. The specific mechanisms of the active ingredients of S. samarangense extract await further investigations.
Keywords: Syzygium samarangense; endothelium; nitric oxide; prostacyclin; vasodilators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vasorelaxant effects of Shunaoxin pill are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, HO/CO pathway and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Sep 15;173:352-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.048. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26239154
-
Vasorelaxant effects of Cerebralcare Granule® are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, potassium channel opening and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):572-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.062. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24924524
-
Syzygium samarangense leaf extract mitigates indomethacin-induced gastropathy via the NF-κB signaling pathway in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jul;139:111675. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111675. Epub 2021 May 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33965725
-
Vasorelaxant and antihypertensive effects of Tianshu Capsule on rats: An in vitro and in vivo approach.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Mar;111:188-197. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.061. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30583226
-
The lignan (-)-cubebin inhibits vascular contraction and induces relaxation via nitric oxide activation in isolated rat aorta.Phytother Res. 2013 Dec;27(12):1784-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4932. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Phytother Res. 2013. PMID: 23401173
Cited by
-
Thymus satureioides Coss. combats oral ulcer via inhibition of inflammation, proteolysis, and apoptosis.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Oct;31(5):2557-2570. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01285-y. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37477794
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

