Data-Driven Technology Roadmaps to Identify Potential Technology Opportunities for Hyperuricemia Drugs
- PMID: 36355529
- PMCID: PMC9694917
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15111357
Data-Driven Technology Roadmaps to Identify Potential Technology Opportunities for Hyperuricemia Drugs
Abstract
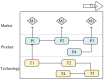
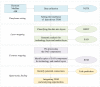
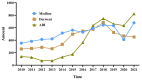
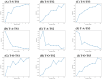
Hyperuricemia is a metabolic disease with an increasing incidence in recent years. It is critical to identify potential technology opportunities for hyperuricemia drugs to assist drug innovation. A technology roadmap (TRM) can efficiently integrate data analysis tools to track recent technology trends and identify potential technology opportunities. Therefore, this paper proposes a systematic data-driven TRM approach to identify potential technology opportunities for hyperuricemia drugs. This data-driven TRM includes the following three aspects: layer mapping, content mapping and opportunity finding. First we deal with layer mapping.. The BERT model is used to map the collected literature, patents and commercial hyperuricemia drugs data into the technology layer and market layer in TRM. The SAO model is then used to analyze the semantics of technology and market layer for hyperuricemia drugs. We then deal with content mapping. The BTM model is used to identify the core SAO component topics of hyperuricemia in technology and market dimensions. Finally, we consider opportunity finding. The link prediction model is used to identify potential technological opportunities for hyperuricemia drugs. This data-driven TRM effectively identifies potential technology opportunities for hyperuricemia drugs and suggests pathways to realize these opportunities. The results indicate that resurrecting the pseudogene of human uric acid oxidase and reducing the toxicity of small molecule drugs will be potential opportunities for hyperuricemia drugs. Based on the identified potential opportunities, comparing the DNA sequences from different sources and discovering the critical amino acid site that affects enzyme activity will be helpful in realizing these opportunities. Therefore, this research provides an attractive option analysis technology opportunity for hyperuricemia drugs.
Keywords: SAO analysis; data-driven TRM; human uric acid oxidase; hyperuricemia drug; link prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Untargeted metabolomics reveal the therapeutic effects of Ermiao wan categorized formulas on rats with hyperuricemia.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;281:114545. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114545. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34419610
-
An integrated study of Shenling Baizhu San against hyperuricemia: Efficacy evaluation, core target identification and active component discovery.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;295:115450. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115450. Epub 2022 Jun 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35688256
-
DKB114, A Mixture of Chrysanthemum Indicum Linne Flower and Cinnamomum Cassia (L.) J. Presl Bark Extracts, Improves Hyperuricemia through Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase Activity and Increasing Urine Excretion.Nutrients. 2018 Sep 28;10(10):1381. doi: 10.3390/nu10101381. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30274153 Free PMC article.
-
Management of hyperuricemia with rasburicase review.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2004 Oct;23(8-9):1431-40. doi: 10.1081/NCN-200027656. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2004. PMID: 15571272 Review.
-
Hyperuricemia: a novel old disorder-relationship and potential mechanisms in heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2020 Jan;25(1):43-51. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09869-z. Heart Fail Rev. 2020. PMID: 31745840 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

