AhR Mediated Activation of Pro-Inflammatory Response of RAW 264.7 Cells Modulate the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- PMID: 36355934
- PMCID: PMC9696907
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10110642
AhR Mediated Activation of Pro-Inflammatory Response of RAW 264.7 Cells Modulate the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Abstract
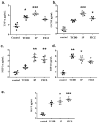
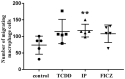
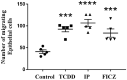
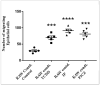
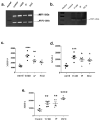
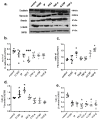
Pulmonary fibrosis, a chronic lung disease caused by progressive deterioration of lung tissue, is generated by several factors including genetic and environmental ones. In response to long-term exposure to environmental stimuli, aberrant tissue repair and epithelial cell-to- mesenchymal cell transition (EMT) trigger the subsequent progression of pulmonary fibrotic diseases. The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a transcription factor that is activated by ligands providing lung dysfunction when activated by environmental toxins, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Our previous study demonstrated that AhR mediates α-SMA expression by directly binding to the α-SMA (fibroblast differentiation marker) promoter, suggesting the role of AhR in mediating fibrogenic progression. Here we follow the hypothesis that macrophage infiltrated microenvironments may trigger inflammation and subsequent fibrosis. We studied the expression of cytokines in RAW 264.7 cells by AhR activation through an ELISA assay. To investigate molecular events, migration, western blotting and zymography assays were carried out. We found that AhR agonists such as TCDD, IP and FICZ, promote the migration and induce inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and G-CSF, MIP-1α, MIP-1β and MIP-2. These cytokines arbitrate EMT marker expression such as E-cadherin, fibronectin, and vimentin in pulmonary epithelial cells. Expression of proteins of MMPs in mouse macrophages was determined by zymography, showing the caseinolytic activity of MMP-1 and the gelatinolytic action of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Taken together, the present study showed that AhR activated macrophages create an inflammatory microenvironment which favours the fibrotic progression of pulmonary epithelial cells. Such production of inflammatory factors was accomplished by affecting the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway, thereby creating a microenvironment which enhances the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, leading to fibrosis of the lung.
Keywords: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; MMP-9; Wnt/β-catenin; epithelial mesenchymal transition; inflammatory cytokines; macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3,3'-Diindolylmethane modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition through repressing RhoA/ROCK1-mediated COX2/PGE2 pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 16;39(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01618-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32546278 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta, accelerates vimentin degradation, and suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Arch Toxicol. 2017 May;91(5):2165-2178. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1870-0. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27752740 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-ligand axis mediates pulmonary fibroblast migration and differentiation through increased arachidonic acid metabolism.Toxicology. 2016 Aug 31;370:116-126. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2016.09.019. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Toxicology. 2016. PMID: 27697457
-
Dioxin receptor expression inhibits basal and transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 15;288(11):7841-7856. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.425009. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23382382 Free PMC article.
-
Direct contribution of epithelium to organ fibrosis: epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Hum Pathol. 2009 Oct;40(10):1365-76. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.02.020. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Hum Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19695676 Review.
Cited by
-
Environmental Toxicant Exposure Paralyzes Human Placental Macrophage Responses to Microbial Threat.ACS Infect Dis. 2023 Dec 8;9(12):2401-2408. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00490. Epub 2023 Nov 13. ACS Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37955242 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Pathway Augments Peritoneal Fibrosis in a Murine CKD Model Exposed to Peritoneal Dialysate.Kidney360. 2024 Sep 1;5(9):1238-1250. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000000000000516. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Kidney360. 2024. PMID: 39235862 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenic Acid/AhR Signaling at the Junction of Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 25;25(13):6933. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136933. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AhR and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways and Their Interplay.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 May 2;45(5):3848-3876. doi: 10.3390/cimb45050248. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37232717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alveolar epithelial cell dysfunction and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis pathogenesis.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Apr 24;12:1564176. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1564176. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40343260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reyfman P.A., Walter J.M., Joshi N., Anekalla K.R., McQuattie-Pimentel A.C., Chiu S., Fernandez R., Akbarpour M., Chen C.-I., Ren Z., et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Lung Provides Insights into the Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019;199:1517–1536. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2410OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ding Q., Sun J., Xie W., Zhang M., Zhang C., Xu X. Stemona alkaloids suppress the positive feedback loop between M2 polarization and fibroblast differentiation by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway in fibroblasts and CXCR4/PI3K/AKT1 pathway in macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019;72:385–394. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.030. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

