Effects of Different Concentrations of Oil Mist Particulate Matter on Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo and In Vitro
- PMID: 36355939
- PMCID: PMC9695344
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10110647
Effects of Different Concentrations of Oil Mist Particulate Matter on Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo and In Vitro
Abstract
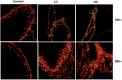
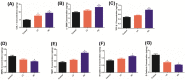
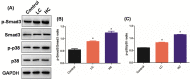
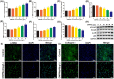
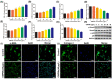
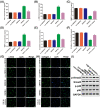
Oil-mist particulate matter (OMPM) refers to oily particles with a small aerodynamic equivalent diameter in ambient air. Since the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis (PF) has not been fully elucidated, this study aims to explore the potential molecular mechanisms of the adverse effects of exposure to OMPM at different concentrations in vivo and in vitro on PF. In this study, rats and cell lines were treated with different concentrations of OMPM in vivo and in vitro. Sirius Red staining analysis shows that OMPM exposure could cause pulmonary lesions and fibrosis symptoms. The expression of TGF-β1, α-SMA, and collagen I was increased in the lung tissue of rats. The activities of MMP2 and TIMP1 were unbalanced, and increased N-Cadherin and decreased E-Cadherin upon OMPM exposure in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, OMPM exposure could activate the TGF-β1/Smad3 and TGF-β1/MAPK p38 signaling pathways, and the differentiation of human lung fibroblast HFL-1 cells. Therefore, OMPM exposure could induce PF by targeting the lung epithelium and fibroblasts, and activating the TGF-β1/Smad3 and TGF-β1/MAPK p38 signaling pathways.
Keywords: OMPM; PF; TGF-β1/MAPK p38; TGF-β1/Smad3.
Conflict of interest statement
This manuscript has not been published in whole or in part and is not being considered for publication elsewhere. This manuscript does not violate or infringe upon any existing copyright/s license/s from any third party. All authors contributed significantly to work and agree with the manuscript’s content. There are no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PM2.5 induced pulmonary fibrosis in vivo and in vitro.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Apr 30;171:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.061. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019. PMID: 30597315
-
Oil mist particulate matter induces myocardial tissue injury by impairing fatty acid metabolism and mitochondrial bioenergetics function via inhibiting the PPAR alpha signaling pathway in rats.Environ Pollut. 2025 Jan 15;365:125340. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.125340. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Environ Pollut. 2025. PMID: 39581367
-
Combined multi-omics analysis reveals oil mist particulate matter-induced lung injury in rats: Pathological damage, proteomics, metabolic disturbances, and lung dysbiosis.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Aug;241:113759. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113759. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 35714485
-
[Effect of epithelial-mesenchymal transition on cardiac fibrosis induced by oil mist particulate matter].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Nov;38(6):633-637. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.6351.2022.115. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 37308408 Chinese.
-
Follistatin-Like 1 Promotes Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through the Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Aug 20;131(16):1917-1925. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.238151. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 30082522 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
BPIFB1 is a prognostic biomarker and mediated collagen synthesis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 30;104(22):e42671. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042671. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40441200 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of short-term exposure to air pollution with risk of pulmonary space-occupying lesions morbidity based on a time-series study.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 9;25(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21245-7. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39789511 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SHANK3 in concentrated ambient PM2. 5 exposure induced autism-like phenotype.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 6;9(3):e14328. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14328. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36938421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fois A.G., Paliogiannis P., Sotgia S., Mangoni A.A., Zinellu E., Pirina P., Carru C., Zinellu A. Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and therapeutic applications: A systematic review. Respir. Res. 2018;19:51. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0754-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

