Effects of Different Concentrations of Oil Mist Particulate Matter on Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo and In Vitro
- PMID: 36355939
- PMCID: PMC9695344
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10110647
Effects of Different Concentrations of Oil Mist Particulate Matter on Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo and In Vitro
Abstract
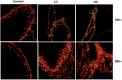
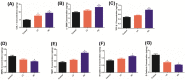
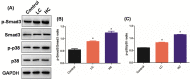
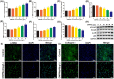
Oil-mist particulate matter (OMPM) refers to oily particles with a small aerodynamic equivalent diameter in ambient air. Since the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis (PF) has not been fully elucidated, this study aims to explore the potential molecular mechanisms of the adverse effects of exposure to OMPM at different concentrations in vivo and in vitro on PF. In this study, rats and cell lines were treated with different concentrations of OMPM in vivo and in vitro. Sirius Red staining analysis shows that OMPM exposure could cause pulmonary lesions and fibrosis symptoms. The expression of TGF-β1, α-SMA, and collagen I was increased in the lung tissue of rats. The activities of MMP2 and TIMP1 were unbalanced, and increased N-Cadherin and decreased E-Cadherin upon OMPM exposure in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, OMPM exposure could activate the TGF-β1/Smad3 and TGF-β1/MAPK p38 signaling pathways, and the differentiation of human lung fibroblast HFL-1 cells. Therefore, OMPM exposure could induce PF by targeting the lung epithelium and fibroblasts, and activating the TGF-β1/Smad3 and TGF-β1/MAPK p38 signaling pathways.
Keywords: OMPM; PF; TGF-β1/MAPK p38; TGF-β1/Smad3.
Conflict of interest statement
This manuscript has not been published in whole or in part and is not being considered for publication elsewhere. This manuscript does not violate or infringe upon any existing copyright/s license/s from any third party. All authors contributed significantly to work and agree with the manuscript’s content. There are no conflict of interest.
Figures
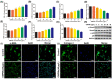
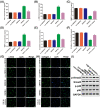
References
-
- Fois A.G., Paliogiannis P., Sotgia S., Mangoni A.A., Zinellu E., Pirina P., Carru C., Zinellu A. Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and therapeutic applications: A systematic review. Respir. Res. 2018;19:51. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0754-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

