Influence of Soil Nutrient Toxicity and Deficiency from Three Ecuadorian Climatic Regions on the Variation of Biological, Metabolic, and Nutritional Properties of Moringa oleifera Lam
- PMID: 36355952
- PMCID: PMC9696296
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10110661
Influence of Soil Nutrient Toxicity and Deficiency from Three Ecuadorian Climatic Regions on the Variation of Biological, Metabolic, and Nutritional Properties of Moringa oleifera Lam
Abstract
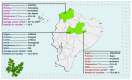
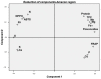
Moringa oleifera Lam. contains numerous essential constituents found in all plant parts (leaves, pods, and seeds). From all its edible parts, the leaf represents an effective remedy with high potential for medicinal applications. Ecuador is part of the new promising cultivation areas for Moringa, and therefore our study is emphasized to determine the influence of soil nutrition, toxicity (excess), and deficiency, from three main areas of this country, correlated with its climatic characteristics, on the mineral components, bioactive compounds' synthesis, and antioxidant capacity of Moringa. Different analyses were performed in soil and especially leaf samples for phytochemical content, antioxidant activity, calcium, protein, and vitamin C determination to identify the relationship between soil nutrients, abiotic conditions, and the therapeutic potential of this species cultivated in Ecuador. The obtained values using methods such as DPPH, FRAP, and ABTS showed a high antioxidant capacity of the leaves from the Coastal Ecuadorian region, related with total phenolic compounds' content (through the Folin-Ciocalteu method) and flavonoids in samples, with results obtained under the positive influence of high soil nutrients such as Ca, Mg, Mn, and Fe. We can conclude that M. oleifera from the coastal area of Ecuador presents the right environmental and soil conditions to positively influence its mineral and phytochemical content, making it suitable for incorporation into foods and medicines to solve the nutritional and medical problems in Ecuador and worldwide.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera Lam.; abiotic components; antioxidant activity; bioactive compounds; toxicity of nutrients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Paliwal R., Sharma V., Pracheta J. A review on horse radish tree (Moringa oleifera): A multipurpose tree with high economic and commercial importance. Asian J. Biotechnol. 2011;3:317–328. doi: 10.3923/ajbkr.2011.317.328. - DOI
-
- Godino M., Arias C., Izquierdo M.I. Moringa oleifera: Potential areas of cultivation on the Iberian Peninsula. Acta Hortic. 2017;1158:405–412. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2017.1158.46. - DOI
-
- Vélez-Gavilán J. Invasive Species Compendium. CABI; Wallingford, UK: 2017. Moringa oleifera (horse radish tree)
-
- Gopalakrishnan L., Kruthi D., Devarai S.K. Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2016;59:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2016.04.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

