Analytical Validation of a Direct Competitive ELISA for Multiple Mycotoxin Detection in Human Serum
- PMID: 36355977
- PMCID: PMC9694295
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14110727
Analytical Validation of a Direct Competitive ELISA for Multiple Mycotoxin Detection in Human Serum
Abstract
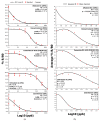
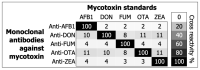
Mycotoxin exposure in humans is primarily assessed through its occurrence in external sources, such as food commodities. Herein, we have developed a direct competitive ELISA to facilitate the detection of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), deoxynivalenol (DON), fumonisin (FUM B1/B2), ochratoxin A (OTA), and zearalenone (ZEA) in human serum. The analytical validation of the assay followed practices endorsed by the international research community and the EU directive 96/23/EC in order to examine detection capability, recovery, and cross-reactivity. The assay demonstrated a lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) for AFB1 [0.61 ng/mL (hereon ng/mL = ppb)], DON (19.53 ppb), FUM (4.88 ppb), OTA (19.53 ppb), and ZEA (0.15 ppb). Recovery from human serum for all mycotoxins spanned from 73% to 106%. Likewise, the specificity for monoclonal antibodies against cross-reactant mycotoxins ranged from 2% to 11%. This study compares the LLOQ and recovery values with commercial and emerging immuno-based methods for detecting mycotoxins in foodstuffs. The LLOQ values from the present study were among the lowest in commercial or emerging methods. Despite the differences in the extraction protocols and matrices, the recovery range in this study, commercial tests, and other procedures were similar for all mycotoxins. Overall, the assay detected AFB1, DON, FUM, OTA, and ZEA in human serum with excellent accuracy, precision, and specificity.
Keywords: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; human biological monitoring; multiple mycotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
Yes, the authors have competing interests as defined by MDPI Toxins or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results or discussion reported herein. Following MDPI Toxins policy, the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests, K.G. and L.G. have a financial and business interest in Tezted Ltd. Further, F.V.-A. and F.S.-R. are employed by the Sanoviv Medical Institute and they do not have commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Sanoviv Medical Institute and Tezted Ltd had no role in experimental design, reporting of the results, or the decision to publish.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A flow cytometry based competitive fluorescent microsphere immunoassay (CFIA) system for detecting up to six mycotoxins.J Immunol Methods. 2012 Oct 31;384(1-2):71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2012.07.010. Epub 2012 Jul 25. J Immunol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22841575
-
Natural occurrence of mycotoxins in staple cereals from Ethiopia.Mycopathologia. 2006 Jul;162(1):57-63. doi: 10.1007/s11046-006-0027-8. Mycopathologia. 2006. PMID: 16830193
-
Co-occurrence of aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, fumonisins, and zearalenone in cereals and feed, determined by competitive direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and thin-layer chromatography.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2009 Dec;60(4):427-34. doi: 10.2478/10004-1254-60-2009-1975. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2009. PMID: 20061243
-
Individual and combined occurrences of the prevalent mycotoxins in commercial feline and canine food.Mycotoxin Res. 2024 Nov;40(4):547-558. doi: 10.1007/s12550-024-00545-2. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Mycotoxin Res. 2024. PMID: 38990416 Review.
-
The efficacy of mycotoxin binders to control mycotoxins in feeds and the potential risk of interactions with nutrient: a review.J Anim Sci. 2022 Nov 1;100(11):skac328. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac328. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 36208465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Aptamer-Based Conjugate Recognition Techniques for the Detection of Small Molecules in Food.Foods. 2024 Jun 2;13(11):1749. doi: 10.3390/foods13111749. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38890976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of distribution of emerging mycotoxins in human tissues: applications of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Jan;416(2):449-459. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-05040-8. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 37987769 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Electrochemiluminescence Biosensors for Mycotoxin Assay.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;13(6):653. doi: 10.3390/bios13060653. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sulyok M., Krska R., Schuhmacher R. A Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometric Multi-Mycotoxin Method for the Quantification of 87 Analytes and Its Application to Semi-Quantitative Screening of Moldy Food Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007;389:1505–1523. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1542-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Binder E.M. Managing the Risk of Mycotoxins in Modern Feed Production. Anim. Feed. Sci. Tech. 2007;133:149–166. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2006.08.008. - DOI
-
- European Commission Decision of 12 August 2002, Implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC Concerning the Performance of Analytical Methods and the Interpretation of Results (2002/657/EC) [(accessed on 27 October 2021)]. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2002:221:000....
-
- European Commission Recommendation 401/2006 of 23 February 2006, Laying Down the Methods of Sampling and Analysis for the Official Control of the Levels of Mycotoxins in Foodstuffs. [(accessed on 28 August 2022)]. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:2006R0401....
-
- Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry. [(accessed on 27 October 2021)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validatio....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

