Current Review of Mycotoxin Biodegradation and Bioadsorption: Microorganisms, Mechanisms, and Main Important Applications
- PMID: 36355979
- PMCID: PMC9694041
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14110729
Current Review of Mycotoxin Biodegradation and Bioadsorption: Microorganisms, Mechanisms, and Main Important Applications
Abstract
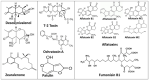
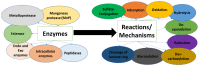
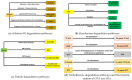
Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by fungi. Food/feed contamination by mycotoxins is a great threat to food safety. The contamination can occur along the food chain and can cause many diseases in humans and animals, and it also can cause economic losses. Many detoxification methods, including physical, chemical, and biological techniques, have been established to eliminate mycotoxins in food/feed. The biological method, with mycotoxin detoxification by microorganisms, is reliable, efficient, less costly, and easy to use compared with physical and chemical ones. However, it is important to discover the metabolite's toxicity resulting from mycotoxin biodegradation. These compounds can be less or more toxic than the parent. On the other hand, mechanisms involved in a mycotoxin's biological control remain still unclear. Mostly, there is little information about the method used by microorganisms to control mycotoxins. Therefore, this article presents an overview of the most toxic mycotoxins and the different microorganisms that have a mycotoxin detoxification ability. At the same time, different screening methods for degradation compound elucidation are given. In addition, the review summarizes mechanisms of mycotoxin biodegradation and gives some applications.
Keywords: aflatoxins; biodegradation; contamination; enzymes; microorganisms; mycotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Environment contamination by mycotoxins and their occurrence in food and feed: Physiological aspects and economical approach.J Environ Sci Health B. 2016;51(4):236-44. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2015.1120617. Epub 2016 Jan 19. J Environ Sci Health B. 2016. PMID: 26786025 Review.
-
Review of mycotoxin reduction in food and feed: from prevention in the field to detoxification by adsorption or transformation.Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2011 Nov;28(11):1590-609. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2011.595377. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2011. PMID: 21770849 Review.
-
Biological Detoxification of Mycotoxins: Current Status and Future Advances.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1064. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031064. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35162993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycotoxin management: exploring natural solutions for mycotoxin prevention and detoxification in food and feed.Mycotoxin Res. 2024 Nov;40(4):519-534. doi: 10.1007/s12550-024-00562-1. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Mycotoxin Res. 2024. PMID: 39271576 Review.
-
Fusarial toxins: secondary metabolites of Fusarium fungi.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;228:101-20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-01619-1_5. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24162094 Review.
Cited by
-
Actinobacteria as Promising Biocontrol Agents for In Vitro and In Planta Degradation and Detoxification of Zearalenone.Toxins (Basel). 2024 May 28;16(6):253. doi: 10.3390/toxins16060253. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38922147 Free PMC article.
-
Abiotic Degradation of the Toxin Simplexin by Soil Collected from a Pimelea-Infested Paddock.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Mar 6;17(3):124. doi: 10.3390/toxins17030124. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137897 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Two Mycotoxin Detoxifications on Laying Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, and Liver Damage of Laying Hens Fed Diet Naturally Contaminated with Low-Level Mycotoxins.Vet Sci. 2025 May 26;12(6):520. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12060520. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40559757 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic assessment of the effect of red yeast (Sporidiobolus pararoseus) as a feed additive on mycotoxin toxicity in laying hens.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 6;14:1254569. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1254569. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37744913 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Enzyme-Based Detoxification Prediction with ToxZyme: An Ensemble Machine Learning Approach.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;17(4):171. doi: 10.3390/toxins17040171. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanzani S.M., Reverberi M., Geisen R. Mycotoxins in harvested fruits and vegetables: Insights in producing fungi, biological role, conducive conditions, and tools to manage postharvest contamination. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016;122:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.07.003. - DOI
-
- Luo Y., Liu X., Li J. Updating techniques on controlling mycotoxins—A review. Food Control. 2018;89:123–132. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.01.016. - DOI
-
- Ünüsan N. Systematic review of mycotoxins in food and feeds in Turkey. Food Control. 2019;97:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.10.015. - DOI
-
- Hoyos Ossa D.E., Hincapié D.A., Peñuela G.A. Determination of aflatoxin M1 in ice cream samples using immunoaffinity columns and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control. 2015;56:34–40. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.03.011. - DOI
-
- Majer-Baranyi K., Zalán Z., Mörtl M., Juracsek J., Szendrő I., Székács A., Adányi N. Optical waveguide lightmode spectroscopy technique-based immunosensor development for aflatoxin B1 determination in spice paprika samples. Food Chem. 2016;211:972–977. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.089. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases