A Pilot Study of A2NTX, a Novel Low-Molecular-Weight Neurotoxin Derived from Subtype A2 for Post-Stroke Lower Limb Spasticity: Comparison with OnabotulinumtoxinA
- PMID: 36355989
- PMCID: PMC9697926
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14110739
A Pilot Study of A2NTX, a Novel Low-Molecular-Weight Neurotoxin Derived from Subtype A2 for Post-Stroke Lower Limb Spasticity: Comparison with OnabotulinumtoxinA
Abstract
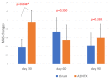
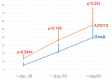
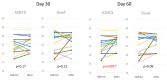
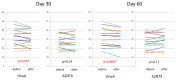
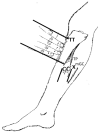
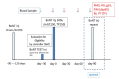
All the currently used type A botulinum neurotoxins for clinical uses are of subtype A1. We compared the efficacy and safety for the first time head-to-head between a novel botulinum toxin A2NTX prepared from subtype A2 and onabotulinumtoxinA (BOTOX) derived from A1 for post-stroke spasticity. We assessed the modified Ashworth scale (MAS) of the ankle joint, the mobility scores of Functional Independence Measure (FIM), and the grip power of the unaffected hand before and after injecting 300 units of BOTOX or A2NTX into calf muscles. The procedure was done in a blinded manner for the patient, the injecting physician, and the examiner. Stroke patients with chronic spastic hemiparesis (15 for A2NTX and 16 for BOTOX) were enrolled, and 11 for A2NTX and 13 for BOTOX (MAS of ankle; > or = 2) were entered for the MAS study. Area-under-curves of changes in MAS (primary outcome) were greater for A2NTX by day 30 (p = 0.044), and were similar by day 60. FIM was significantly improved in the A2NTX group (p = 0.005), but not in the BOTOX group by day 60. The hand grip of the unaffected limb was significantly decreased in the BOTOX-injected group (p = 0.002), but was unaffected in the A2NTX-injected group by day 60, suggesting there was less spread of A2NTX to the upper limb than there was with BOTOX. Being a small-sized pilot investigation with an imbalance in the gender of the subjects, the present study suggested superior efficacy and safety of A2NTX, and warrants a larger scale clinical trial of A2NTX to confirm these preliminary results.
Keywords: A2NTX; Functional Independence Measure; botulinum neurotoxin; clinical efficacy; hand grip; onabotulinumtoxinA; safety; spasticity: modified Ashworth scale; spread; subtype A2.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent on A2NTX (WO 2008/050866) is owned by Tokushima University and Shionogi Pharma, Osaka, Japan.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical differences between A1 and A2 botulinum toxin subtypes.Toxicon. 2015 Dec 1;107(Pt A):85-8. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.09.025. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Toxicon. 2015. PMID: 26394198 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of NABOTA in post-stroke upper limb spasticity: a phase 3 multicenter, double-blinded, randomized controlled trial.J Neurol Sci. 2015 Oct 15;357(1-2):192-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.07.028. Epub 2015 Jul 21. J Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26233808 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Safety and Tolerability of A2NTX, a Novel Low-Molecular-Weight Neurotoxin Derived from Botulinum Neurotoxin Subtype A2, in Comparison with Subtype A1 Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;13(11):824. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110824. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34822610 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of letibotulinumtoxinA(BOTULAX®) in treatment of post stroke upper limb spasticity: a randomized, double blind, multi-center, phase III clinical trial.Clin Rehabil. 2017 Sep;31(9):1179-1188. doi: 10.1177/0269215516689331. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Clin Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 28118733 Clinical Trial.
-
[Botulinum toxin treatment of hip adductor spasticity in multiple sclerosis].Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001;113 Suppl 4:20-4. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001. PMID: 15506048 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A (BoNT-A) on Muscle Strength in Adult-Onset Neurological Conditions with Focal Muscle Spasticity: A Systematic Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;16(8):347. doi: 10.3390/toxins16080347. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195757 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

