Neurophysiological Basis of Deep Brain Stimulation and Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection for Treating Oromandibular Dystonia
- PMID: 36356002
- PMCID: PMC9694803
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14110751
Neurophysiological Basis of Deep Brain Stimulation and Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection for Treating Oromandibular Dystonia
Abstract
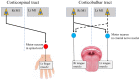
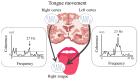
Oromandibular dystonia (OMD) induces severe motor impairments, such as masticatory disturbances, dysphagia, and dysarthria, resulting in a serious decline in quality of life. Non-invasive brain-imaging techniques such as electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) are powerful approaches that can elucidate human cortical activity with high temporal resolution. Previous studies with EEG and MEG have revealed that movements in the stomatognathic system are regulated by the bilateral central cortex. Recently, in addition to the standard therapy of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) injection into the affected muscles, bilateral deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been applied for the treatment of OMD. However, some patients' OMD symptoms do not improve sufficiently after DBS, and they require additional BoNT therapy. In this review, we provide an overview of the unique central spatiotemporal processing mechanisms in these regions in the bilateral cortex using EEG and MEG, as they relate to the sensorimotor functions of the stomatognathic system. Increased knowledge regarding the neurophysiological underpinnings of the stomatognathic system will improve our understanding of OMD and other movement disorders, as well as aid the development of potential novel approaches such as combination treatment with BoNT injection and DBS or non-invasive cortical current stimulation therapies.
Keywords: botulinum neurotoxin; deep brain stimulation; electroencephalography; globus pallidus; magnetoencephalography; motor function; oromandibular dystonia; sensorimotor function; stomatognathic function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

