An Eight-Year Survey on Aflatoxin B1 Indicates High Feed Safety in Animal Feed and Forages in Northern Italy
- PMID: 36356013
- PMCID: PMC9699321
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14110763
An Eight-Year Survey on Aflatoxin B1 Indicates High Feed Safety in Animal Feed and Forages in Northern Italy
Abstract
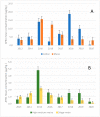
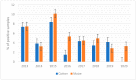
Aflatoxins (AFs) remain the main concern for the agricultural and dairy industries due to their effects on the performances and quality of livestock production. Aflatoxins are always unavoidable and should be monitored. The objective of this paper is to bring to light a significant volume of data on AF contamination in several animal feed ingredients in Northern Italy. The Regional Breeders Association of Lombardy has been conducting a survey program to monitor mycotoxin contamination in animal feeds, and in this paper, we present data relating to AFB1 contamination. In most cases (95%), the concentrations were low enough to ensure compliance with the European Union's (EU's) maximum admitted levels for animal feed ingredients. However, the data show a high variability in AF contamination between different matrices and, within the same matrix, a high variability year over year. High levels of AFs were detected in maize and cotton, especially in the central part of the second decade of this century, i.e., 2015-2018, which has shown a higher risk of AF contamination in feed materials in Northern Italy. Variability due to climate change and the international commodity market affect future prospects to predict the presence of AFs. Supplier monitoring and control and reduced buying of contaminated raw materials, as well as performing analyses of each batch, help reduce AF spread.
Keywords: AFB1; aflatoxins; animal feed; maize; monitoring program; mycotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Compliance between Food and Feed Safety: Eight-Year Survey (2013-2021) of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw Milk and Aflatoxin B1 in Feed in Northern Italy.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;15(3):168. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030168. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977059 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of the analytical control of aflatoxins in feedstuffs for dairy cows for the prevention of aflatoxin M1 in milk.Mycotoxin Res. 2020 Feb;36(1):11-22. doi: 10.1007/s12550-019-00362-y. Epub 2019 May 14. Mycotoxin Res. 2020. PMID: 31111427
-
Aflatoxins and fumonisins co-contamination effects on laying hens and use of mycotoxin detoxifiers as a mitigation strategy.Mycotoxin Res. 2025 Feb;41(1):63-75. doi: 10.1007/s12550-024-00566-x. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Mycotoxin Res. 2025. PMID: 39402398 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-mycotoxin occurrence in feed, metabolism and carry-over to animal-derived food products: A review.Food Chem Toxicol. 2021 Dec;158:112661. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112661. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34762978 Review.
-
Comprehensive Review of Aflatoxin Contamination, Impact on Health and Food Security, and Management Strategies in Pakistan.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Dec 2;14(12):845. doi: 10.3390/toxins14120845. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36548742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring Mycotoxin Exposure in Food-Producing Animals (Cattle, Pig, Poultry, and Sheep).Toxins (Basel). 2024 May 9;16(5):218. doi: 10.3390/toxins16050218. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38787070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring of Animal Feed Contamination by Mycotoxins: Results of Five Years of Official Control by an Accredited Italian Laboratory.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 15;12(1):173. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010173. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38257999 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin attenuates aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity via suppressing c-Jun-N-terminal kinase-mediated cell apoptosis.Mycotoxin Res. 2024 Aug;40(3):457-466. doi: 10.1007/s12550-024-00540-7. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Mycotoxin Res. 2024. PMID: 38913091
-
Pre-Harvest Aflatoxin Contamination in Crops and Climate Change Factors: A European Overview.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;17(7):344. doi: 10.3390/toxins17070344. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycotoxins evaluation of total mixed ration (TMR) in bovine dairy farms: An update.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 6;10(4):e25693. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25693. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38370215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pinotti L., Ferrari L., Rovere N., Fumagalli F., Mazzoleni S., Cheli F. Advances in Understanding Key Contamination Risks in Animal Feed: Mycotoxins. Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing Limited; Cambridge, UK: 2021. - DOI
-
- Cheli F., Fumagalli F., Ottoboni M., Pinotti L. Cereal-Based Foodstuffs: The Backbone of Mediterranean Cuisine. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. Safety of Cereals in the Mediterranean: An Update on EU Legislation. - DOI

