Antinociceptive Effect of a Sacro-Coccygeal Epidural of Morphine and Lidocaine in Cats Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy
- PMID: 36356100
- PMCID: PMC9698262
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci9110623
Antinociceptive Effect of a Sacro-Coccygeal Epidural of Morphine and Lidocaine in Cats Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy
Abstract
Background: A commonly described analgesic protocol for ovariohysterectomy (OHE) combines systemic opioids, sedatives, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, systemic analgesia does not fully prevent perioperative visceral and somatic pain triggered by the surgical stimulus.
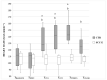
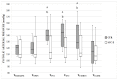
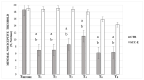
Objectives: To compare the analgesic effects and quality of recovery of systemic analgesia with those of a sacrococcygeal epidural injection of lidocaine and morphine in cats undergoing elective OHE. Methods: Twenty domestic female cats were premedicated with dexmedetomidine (0.01 mg kg-1 IM) and alfaxalone (1.5 mg kg-1 IM) and randomly assigned to one of two analgesic protocols: methadone (0.2 mg kg-1 IM) in the control group CTR (n = 10) and methadone (0.1 mg kg-1 IM) + epidural (lidocaine 2% (0.3 mL kg-1) + morphine 1% (0.1 mg kg-1) diluted with NaCl 0.9% to a total volume of 1.5 mL in the SCC-E group (n = 10). General anaesthesia was induced with alfaxalone (1 mg kg-1 IV) and maintained with sevoflurane in 100% oxygen. Non-invasive blood arterial pressure and cardiorespiratory variables were recorded. The quality of recovery was assessed using a simple descriptive scale. Before surgery and 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 h post-op pain was assessed using the UNESP-Botucatu multidimensional composite pain scale (MCPS) and mechanical nociception thresholds (MNT). The repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare groups over time. Comparison between groups was performed using independent samples t-test if the assumption of normality was verified, or the Mann-Whitney test. The chi-square test of independence and exact Fisher's test were used to compare groups according to recovery quality.
Results: Heart rate and systolic arterial pressure increased significantly from baseline values in the CTR group and did not change in the SCC-E group. In the CTR group, MNT and UNESP-Botucatu-MCPS scores increased significantly from baseline for all assessment points and the first 3 h, respectively, whereas this did not occur in the SCC-E group.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: Based on our results, the SCC-E administration of lidocaine 2% with morphine 1% is a reasonable option to provide perioperative analgesia in cats submitted to OHE, compared to a systemic protocol alone.
Keywords: analgesia; antinociceptive; cat; epidural; locoregional anaesthesia; ovariohysterectomy; pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of intratesticular lidocaine, sacrococcygeal epidural lidocaine and intravenous methadone in cats undergoing castration: a prospective, randomized, investigator-blind clinical trial.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2017 Mar;44(2):356-363. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2016.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 28455211 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Lidocaine Injection at Acupuncture Points on Perioperative Analgesia in Cats Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy.J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2022 Aug 31;15(4):255-263. doi: 10.51507/j.jams.2022.15.4.255. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2022. PMID: 36521774
-
Comparison of the effects of buprenorphine and methadone in combination with medetomidine followed by intramuscular alfaxalone for anaesthesia of cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy.J Feline Med Surg. 2020 Feb;22(2):77-83. doi: 10.1177/1098612X19826357. Epub 2019 Feb 5. J Feline Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 30719951 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intraperitoneal ropivacaine and ropivacaine-dexmedetomidine for postoperative analgesia in cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2020 May;47(3):396-404. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2020.01.007. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 32199795
-
Comparison of perioperative analgesia using the infiltration of the surgical site with ropivacaine alone and in combination with meloxicam in cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Mar 16;16(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02303-9. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32178668 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pain Management in Animals with Oncological Disease: Opioids as Influencers of Immune and Tumor Cellular Balance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 29;16(17):3015. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173015. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Analgesic Efficacy of Lumbosacral Epidural Morphine in Cats Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy: A Comparative Study of Two Doses.Vet Sci. 2024 Aug 9;11(8):360. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11080360. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39195814 Free PMC article.
-
Can a Sacrococcygeal Epidural of 0.25% Bupivacaine Prevent the Activation of the Sympathetic Nervous System during Feline Ovariectomy?Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 8;14(12):1732. doi: 10.3390/ani14121732. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929350 Free PMC article.
-
Anaesthesia in Veterinary Oncology: The Effects of Surgery, Volatile and Intravenous Anaesthetics on the Immune System and Tumour Spread.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 1;13(21):3392. doi: 10.3390/ani13213392. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison between Bilateral Ultrasound-Guided Quadratus Lumborum Block and Sacrococcygeal Epidural in Cats Undergoing Ovariectomy.Vet Sci. 2024 Jan 8;11(1):25. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11010025. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38250931 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

