A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase II study to evaluate the tolerability of an induction dose escalation of everolimus in patients with metastatic breast cancer (DESIREE)
- PMID: 36356410
- PMCID: PMC9832733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100601
A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase II study to evaluate the tolerability of an induction dose escalation of everolimus in patients with metastatic breast cancer (DESIREE)
Abstract
Background: Stomatitis is one of the main reasons to discontinue everolimus in patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+)/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) metastatic breast cancer (mBC). To decrease stomatitis and subsequently early treatment discontinuations or dose reductions, the DESIREE trial investigated the use of a stepwise dose-escalation schedule of everolimus (EVE esc).
Patients and methods: DESIREE is a phase II, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with HR+/HER2- mBC and progression/relapse after nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor treatment. Patients were randomised to EVE esc (2.5 mg/day, week 1; 5 mg/day, week 2; 7.5 mg/day, week 3; 10 mg/day, weeks 4-24) or everolimus 10 mg/day (EVE 10mg) for 24 weeks plus exemestane. The primary endpoint was the incidence of stomatitis episodes grade ≥2 within 12 weeks of treatment. The secondary endpoints included toxicity, relative total dose intensity (RTDI) and quality of life (QoL).
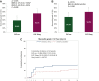
Results: A total of 160 patients were randomised and 156 started treatment (EVE esc: 80; EVE 10mg: 76). The median age of patients was 64 years (range 33-85), 56.3% patients in the EVE esc arm versus 42.1% in the EVE 10mg arm had liver metastasis (P = 0.081) and 62.5% versus 51.3% received over one metastatic therapy line (P = 0.196). Within 12 weeks, the incidence of stomatitis episodes grade ≥2 was significantly lower in the EVE esc arm compared with the EVE 10mg arm (28.8% versus 46.1%; odds ratio 0.47, 95% confidence interval 0.24-0.92; P = 0.026). Toxicity was in line with the known safety profile without new safety concerns. The median RTDI was 91.1% in the EVE esc arm versus 80.0% in the EVE 10mg arm (P = 0.329). Discontinuation rate in the first 3 weeks was 6.3% versus 15.8%, respectively (P = 0.073). QoL was comparable between the two treatment arms.
Conclusions: A dose-escalation schema of everolimus over 3 weeks can be successfully used to reduce the incidence of high-grade stomatitis in the first 12 weeks of treatment in patients with HR+/HER2- mBC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.govNCT02387099; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02387099.
Keywords: everolimus; exemestane; metastatic breast cancer; stomatitis.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure VM reports personal fees from Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Pfizer, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Teva, Seagen, GSK, Gilead; personal fees from Genomic Health, Gilead, Hexal, Roche, Pierre Fabre, Amgen, Clin Sol, Novartis, MSD, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Lilly, GSK, Gilead, other from Novartis, Roche, Seagen, Genentech, outside the submitted work. MS reports grants or contracts to the Institution from AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Eisai, German Breast Group, Genentech, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Eisai, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Seagen; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Seagen; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Pfizer and Roche; patents planned, issued or pending: EP 2951317 B1 and EP 2390370 B1; participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Lilly, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Seagen; receipt of equipment, materials, drugs, medical writing, gifts or other services from Roche. MR reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Novartis, Pfizer; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Novartis, Pfizer. TD reports consulting fees from Novartis Adboard, iOMEDICO adboard. TL reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Amgen, Roche, Clovis, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Lilly, GSK, Gilead, AstraZeneca; support for attending meetings and/or travel from MSD, Celgene, Clovis, Gilead, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer; participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Amgen, MSD, Roche, Tesaro, Pfizer, Lilly, Myriad, Eisai, GSK, Daiichi Sankyo. KL reports payment for participation on Advisory Board from Seagen, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Genomic Health, Roche, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Eisai; payment or honoraria for lectures from Novartis, Genomic Health, Roche, Lilly. MT reports trial funding, payment to the institution from Exact Sciences, Endomag; consulting fees or Advisory board from Agendia, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Becton/Dickinson, ClearCut, Clovis, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Exact Sciences, Gilead, Grünenthal, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Neodynamics, Onkowissen, Organon, Pfizer, Pfm medical, Pierre-Fabre, Roche, Seagen, Sirius Pintuition, Sysmex; payment or honoraria for lectures, manuscript writing from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Art tempi, ClearCut, Clovis, Connect Medica, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Gilead, Hexal, Exact Sciences, Eickeler, Onkowissen, Sysmex, Vifor, Viatris, I-Med-Institute, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, pfm medical, Roche, Seagen, Servier; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Amgen, Art tempi, AstraZeneca, Clearcut, Clovis, Connect medica, Daiichi Sankyo, Exact Sciences, I-Med-Institute, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, pfm medical, Neodynamics, Seagen; leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group, paid or unpaid from AWOgyn. MvM reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Genomic Health, Gilead, GSK, Lilly, Molecular Health, Mylan, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Seagen; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Lilly. SL reports honoraria for Advisory board, lectures and research grant paid to the institution from Novartis, AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Pfizer, Roche; advisory board and research grant paid to the institution from AbbVie, BMS (Celgene), Gilead; honoraria for advisory board paid to the institution from Amgen, EirGenix, GSK, Lilly, Merck KGaA, Pierre-Fabre, Sanofi; honoraria for Advisory board and medical writing paid to the institution, and nonfinancial support from Seagen; patent issued and royalties (Digital Ki67 Evaluator) VM Scope GmbH paid to the institution; patents pending: EP14153692.0 (immunosignature in TNBC), EP21152186.9 (signature for CDK4/6 inhibitor), EP19808852.8. (GeparNUEVO) paid to the institution; patent issued: EP15702464.7 (Predicting response to an anti-HER2 containing therapy) paid to the institution. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. Data sharing
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety of everolimus plus exemestane in patients with hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer progressing on prior non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors: primary results of a phase IIIb, open-label, single-arm, expanded-access multicenter trial (BALLET).Ann Oncol. 2016 Sep;27(9):1719-25. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw249. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27358383 Clinical Trial.
-
Prevention of everolimus-related stomatitis in women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer using dexamethasone mouthwash (SWISH): a single-arm, phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2017 May;18(5):654-662. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30109-2. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28314691 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of everolimus with exemestane vs. exemestane alone in elderly patients with HER2-negative, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in BOLERO-2.Clin Breast Cancer. 2013 Dec;13(6):421-432.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2013.08.011. Clin Breast Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24267730 Clinical Trial.
-
Everolimus: a new hope for patients with breast cancer.Curr Med Res Opin. 2014 Jan;30(1):75-87. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.846253. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014. PMID: 24050600 Review.
-
Everolimus-based combination therapies for HR+, HER2- metastatic breast cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2018 Sep;69:204-214. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.07.013. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018. PMID: 30092555 Review.
Cited by
-
The prognosis of patients treated with everolimus for advanced ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer is driven by molecular features.J Pathol Clin Res. 2024 May;10(3):e12372. doi: 10.1002/2056-4538.12372. J Pathol Clin Res. 2024. PMID: 38563252 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of advanced breast cancer in China (2022 edition).J Natl Cancer Cent. 2023 Dec 18;4(2):107-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2023.12.001. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Natl Cancer Cent. 2023. PMID: 39282589 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the effectiveness and safety of surufatinib versus everolimus or sunitinib in advanced neuroendocrine neoplasms: insights from a real-world, retrospective cohort study using propensity score and inverse probability treatment weighting analysis.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Apr 30;15(2):689-709. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-218. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38756630 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Results with Everolimus in Advanced Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer in a Multicenter National Real-World Observational Study.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 13;15(4):1191. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041191. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831532 Free PMC article.
-
Skipping a pillar does not make for strong foundations: Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic reasoning behind the shape of dose-response relationships in oncology.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;12(11):1591-1601. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13020. Epub 2023 Sep 28. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37771203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rugo H.S., Rumble R.B., Macrae E., et al. Endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:3069–3103. - PubMed
-
- Murphy C.G., Dickler M.N. Endocrine resistance in hormone-responsive breast cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016;23:R337–R352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

