Lipidomic signatures align with inflammatory patterns and outcomes in critical illness
- PMID: 36357394
- PMCID: PMC9647252
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34420-4
Lipidomic signatures align with inflammatory patterns and outcomes in critical illness
Abstract
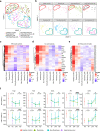
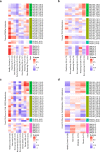
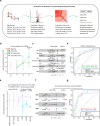
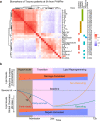
Alterations in lipid metabolism have the potential to be markers as well as drivers of pathobiology of acute critical illness. Here, we took advantage of the temporal precision offered by trauma as a common cause of critical illness to identify the dynamic patterns in the circulating lipidome in critically ill humans. The major findings include an early loss of all classes of circulating lipids followed by a delayed and selective lipogenesis in patients destined to remain critically ill. The previously reported survival benefit of early thawed plasma administration was associated with preserved lipid levels that related to favorable changes in coagulation and inflammation biomarkers in causal modelling. Phosphatidylethanolamines (PE) were elevated in patients with persistent critical illness and PE levels were prognostic for worse outcomes not only in trauma but also severe COVID-19 patients. Here we show selective rise in systemic PE as a common prognostic feature of critical illness.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Lipidomic Signatures Align with Inflammatory Patterns and Outcomes in Critical Illness.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2021 Jan 8:rs.3.rs-106579. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-106579/v1. Res Sq. 2021. Update in: Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 10;13(1):6789. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34420-4. PMID: 33442677 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Davidson GH, et al. Long-term survival of adult trauma patients. JAMA. 2011;305:1001–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

