Effect of the sagittal osteotomy inclination angle on the posterior tibial slope change in high tibial osteotomy: three-dimensional simulation study
- PMID: 36357467
- PMCID: PMC9649806
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23412-5
Effect of the sagittal osteotomy inclination angle on the posterior tibial slope change in high tibial osteotomy: three-dimensional simulation study
Abstract
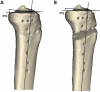
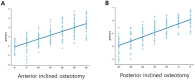
In performing medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy, it is recommended not to alter the posterior tibial slope. However, it remains unclear whether the osteotomy inclination angle affects the posterior tibial slope in the sagittal plane. This study aimed to verify how anterior or posterior osteotomy inclination angle affects the tendency of change in the posterior tibial slope and to conduct quantitative analysis of the extent to which the posterior tibial slope changes according to the degree of the osteotomy inclination angle change in MOWHTO. Computed tomography images of 30 patients who underwent MOWHTO were collected. Three-dimensional models of preoperative original tibia were reconstructed, and virtual osteotomies were performed. The sagittal osteotomy inclination angles formed by the osteotomy line and the medial tibial plateau line were classified as positive in case of anteriorly inclined osteotomy and negative in case of posteriorly inclined osteotomy. Thirteen osteotomies were performed for each tibial model at intervals of 5° from - 30° to 30°. The posterior tibial slope was assessed, and the proportional relationship between the sagittal osteotomy inclination angle and the posterior tibial slope change was analyzed. The posterior tibial slope changed significantly after osteotomy (p < 0.001), except for the cases where the sagittal osteotomy inclination angles were 5°, 0°, and - 5°. Anteriorly and posteriorly inclined osteotomy caused increase and decrease in the posterior tibial slope, respectively. As the inclination angle increased by 1°, the posterior tibial slope increased by 0.079° in anterior inclination osteotomy, while in posterior inclination osteotomy, as the inclination angle decreased by 1°, the posterior tibial slope decreased by 0.067°. The osteotomy inclination angle in the sagittal plane significantly affected the posterior tibial slope. When there was an inclination angle occurred between the osteotomy line and the medial tibial plateau line in the sagittal plane, the posterior tibial slope changed after MOWHTO. The posterior tibial slope tended to increase in anteriorly inclined osteotomy and decrease in posteriorly inclined osteotomy. The change in the posterior tibial slope was proportionally related to the absolute value of the osteotomy inclination angle.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
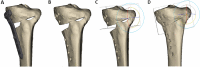
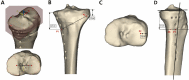
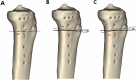
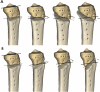
References
-
- Coventry, M. B. Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee. A preliminary report. 1965. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 4–8 (1989). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

