Assessment of ground deformation and seismicity in two areas of intense hydrocarbon production in the Argentinian Patagonia
- PMID: 36357519
- PMCID: PMC9649598
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23160-6
Assessment of ground deformation and seismicity in two areas of intense hydrocarbon production in the Argentinian Patagonia
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Assessment of ground deformation and seismicity in two areas of intense hydrocarbon production in the Argentinian Patagonia.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 6;13(1):307. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26998-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36609458 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
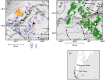
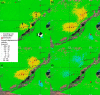
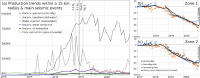
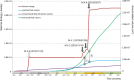
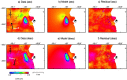
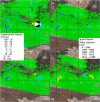
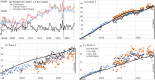
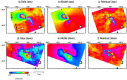
The exploitation of both conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons may lead to still not well-known environmental consequences such as ground deformation and induced/triggered seismicity. Identifying and characterizing these effects is fundamental for prevention or mitigation purposes, especially when they impact populated areas. Two case studies of such effects on hydrocarbon-producing basins in Argentina, the Neuquén and the Golfo de San Jorge, are presented in this work. The intense hydrocarbon production activities in recent years and their potential link with the occurrence of two earthquakes of magnitude 4.9 and 5 near the operating well fields is assessed. A joint analysis of satellite radar interferometry and records of fluid injection and extraction demonstrate that, between 2017 and 2020, vertical ground displacements occurred in both study areas over active well fields that might indicate a correlation to hydrocarbon production activities. Coseismic deformation models of the two earthquakes constrain source depths to less than 2 km. The absence of seismicity before the beginning of the hydrocarbon activities in both areas, and the occurrence of the two largest and shallow earthquakes in the vicinity of the active well fields just after intensive production periods, points towards the potential association between both phenomena.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between localized geohazards in West Texas and human activities, recognized by Sentinel-1A/B satellite radar imagery.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 16;8(1):4727. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23143-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29549321 Free PMC article.
-
Author Correction: Assessment of ground deformation and seismicity in two areas of intense hydrocarbon production in the Argentinian Patagonia.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 6;13(1):307. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26998-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36609458 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prevention of Disasters Related to Extreme Natural Ground Deformation Events by Applying Spatial Modeling in Urban Areas (Quito, Ecuador).Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 24;17(3):753. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17030753. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31991618 Free PMC article.
-
A risk-mitigation approach to the management of induced seismicity.J Seismol. 2015;19(2):623-646. doi: 10.1007/s10950-015-9478-z. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Seismol. 2015. PMID: 28190961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statistical physics models for aftershocks and induced seismicity.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2018 Nov 26;377(2136):20170397. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2017.0397. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2018. PMID: 30478209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
InSAR data for detection and modelling of overexploitation-induced subsidence: application in the industrial area of Prato (Italy).Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 2;14(1):17950. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67725-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39095514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semple AG, Pritchard ME, Lohman RB. An incomplete inventory of suspected human-induced surface deformation in North America detected by satellite interferometric synthetic-aperture radar. Remote Sens. 2017;9:1296. doi: 10.3390/rs9121296. - DOI
-
- Segall P, Grasso J-R, Mossop A. Poroelastic stressing and induced seismicity near the Lacq gas field, southwestern France. J. Geophys. Res. 1994;99(B8):15423–15438. doi: 10.1029/94JB00989. - DOI
-
- Van Thienen-Visser K, Breunese JN. Induced seismicity of the Groningen gas field: History and recent developments. Lead. Edge. 2015;34(6):664–671. doi: 10.1190/tle34060664.1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

