Identification of risk factors for venous thromboembolism and validation of the Khorana score in patients with advanced lung cancer: based on the multicenter, prospective Rising-VTE/NEJ037 study data
- PMID: 36357710
- PMCID: PMC9823025
- DOI: 10.1007/s10147-022-02257-y
Identification of risk factors for venous thromboembolism and validation of the Khorana score in patients with advanced lung cancer: based on the multicenter, prospective Rising-VTE/NEJ037 study data
Abstract
Background: Management of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism (VTE) is essential in cancer treatment selection and prognosis. However, currently, no method exists for assessing VTE risk associated with advanced lung cancer. Therefore, we assessed VTE risk, including driver gene mutation, in advanced lung cancer and performed a Khorana score validation.
Methods: The Rising-VTE/NEJ037 study was a multicenter prospective observational study that included patients with advanced lung cancer. In the Rising-VTE/NEJ037 study, the Khorana score was calculated for enrolled patients with available data on all Khorana score components. The modified Khorana score was based on the body mass index of ≥ 25 kg/m2, according to the Japanese obesity standard. A multivariate logistic regression analysis, including patient background characteristics, was performed to evaluate the presence of VTE 2 years after the lung cancer diagnosis.
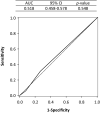
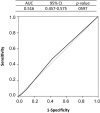
Results: This study included 1008 patients with lung cancer, of whom 100 (9.9%) developed VTE. From the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, VTE risk could not be determined because both the Khorana score (0.518) and modified Khorana score (0.516) showed very low areas under the curve. The risk factors for VTE in the multivariate analysis included female sex, adenocarcinoma, performance status, N factor, lymphocyte count, platelet count, prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 and diastolic blood pressure.
Conclusion: The Khorana score, which is widely used in cancer-VTE risk assessment, was less useful for Japanese patients with advanced lung cancer. Prothrombin fragment 1 + 2, a serum marker involved in coagulation, was more suitable for risk identification.
Clinical trial information: jRCTs061180025.
Keywords: Deep vein thrombosis; Khorana score; Lung cancer; Prothrombin fragment 1 + 2; Pulmonary thromboembolism.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Yukari Tsubata received grant and personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. and AstraZeneca K.K. and personal fees from Chugai Pharmaceuticals Inc. outside the submitted work. Naoki Furuya received personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., MSD K.K., Pfizer Japan Inc. Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Novartis Pharma K.K. outside the submitted work. Toshihide Yokoyama received personal fees from Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Merck Sharp & Dohme K.K., Takeda Pharmaceutical outside the submitted work. Atsushi Nakamura received grant and personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., Pfizer Japan Inc., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., and personal fees from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., outside the submitted work. Takeshi Masuda received personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., outside the submitted work. Kazunori Fujitaka received personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, MSD K.K., Pfizer Japan Inc., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan, and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work. Kunihiko Kobayashi received personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Takeda Pharmaceutical outside the submitted work. Takeshi Isobe received grant and personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Pfizer Japan Inc., and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., and grants from Pearl Therapeutics Inc. and Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new risk-assessment tool for venous thromboembolism in advanced lung cancer: a prospective, observational study.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Apr 4;15(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01259-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35379309 Free PMC article.
-
A Clinical-Genetic Risk Score for Predicting Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism: A Development and Validation Study Involving Two Independent Prospective Cohorts.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun 1;41(16):2911-2925. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00255. Epub 2023 Feb 2. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36730884 Free PMC article.
-
A modified Khorana score as a risk assessment tool for predicting venous thromboembolism in newly diagnosed advanced lung cancer.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 Oct;52(3):898-903. doi: 10.1007/s11239-021-02396-5. Epub 2021 Feb 18. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 33599857
-
[Predicting the Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism Using the Khorana Score: A Literature Review].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2021;141(4):611-622. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.20-00228. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2021. PMID: 33790126 Review. Japanese.
-
External validation of the Khorana score for the prediction of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Nurs Stud. 2024 Nov;159:104867. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2024.104867. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Int J Nurs Stud. 2024. PMID: 39151210
Cited by
-
Lung Cancer Related Thrombosis (LCART): Focus on Immune Checkpoint Blockade.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 20;16(2):450. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020450. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Incidence and Risk Factors of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma Receiving Anti-tumor Therapy].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2023 Jun 20;26(6):439-448. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.102.22. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37488081 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A Predictive Model for Cancer-Associated Thrombosis in Japanese Cancer Patients: Findings from the J-Khorana Registry.TH Open. 2024 Jan 8;8(1):e9-e18. doi: 10.1055/a-2207-7715. eCollection 2024 Jan. TH Open. 2024. PMID: 38197014 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of risk assessment scores in predicting venous thromboembolism in patients with lung cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Oct 10;24(1):507. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03323-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39390440 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial Thromboembolism in Patients With Advanced Lung Cancer: Secondary Analyses of the Rising-VTE/NEJ037 Study.Cancer Med. 2025 Jan;14(1):e70568. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70568. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39783855 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

