Long-term Relugolix Combination Therapy for Symptomatic Uterine Leiomyomas
- PMID: 36357960
- PMCID: PMC9665945
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004988
Long-term Relugolix Combination Therapy for Symptomatic Uterine Leiomyomas
Abstract
Objective: In the LIBERTY 1 and LIBERTY 2 placebo-controlled trials, once-daily relugolix combination therapy reduced menstrual blood loss volume and pain in women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine leiomyomas and was well tolerated, with preservation of bone mineral density (BMD) through 24 weeks. Here we report the long-term efficacy and safety of relugolix combination therapy treatment for up to 52 weeks.
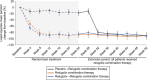
Methods: Women with uterine leiomyoma-associated heavy menstrual bleeding who completed any treatment arm in either the LIBERTY 1 or LIBERTY 2 trial were eligible to enroll in a 28-week long-term extension study. All participants received once-daily relugolix combination therapy (40 mg relugolix, estradiol 1 mg, norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg) in the extension study. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of women who achieved or maintained a menstrual blood loss volume of less than 80 mL and a 50% or greater reduction in menstrual blood loss volume from LIBERTY study baseline to the last 35 days of treatment (defined as responders ). Analyses were conducted for all three randomized treatment groups from pivotal studies.
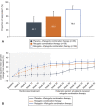
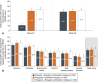
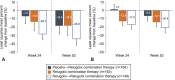
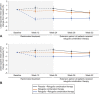
Results: Overall, 477 women enrolled, 476 were treated, and 363 (76.1%) completed 52 weeks. Among patients treated with relugolix combination therapy through 52 weeks (n=163), sustained improvement in heavy menstrual bleeding was observed in 87.7% (responders). The least squares mean menstrual blood loss volume reduction was 89.9%, with 70.6% of patients achieving amenorrhea. At week 52, 59.0% of patients with anemia at baseline had improvements in hemoglobin concentration of greater than 2 g/dL. Distress due to uterine leiomyoma-associated symptoms measured by the BPD (Bleeding and Pelvic Discomfort) scale score was reduced by 51.3 points. Sustained reductions in uterine and uterine leiomyoma volume were observed. Bone mineral density was preserved through week 52.
Conclusion: Improvements in heavy menstrual bleeding and anemia and reduction of uterine leiomyoma-associated symptom burden were sustained through up to 52 weeks of treatment with relugolix combination therapy in women with uterine leiomyomas. No new safety concerns were identified, and BMD was maintained.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov , NCT03049735; NCT03103087; NCT03412890.
Funding source: Myovant Sciences GmbH.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosure Ayman Al-Hendy has been a Consultant for AbbVie, Bayer, Myovant Sciences, and ObsEva. They have received Research Support from the National Institutes of Health (R01 ES 028615–01, R01HD 087417, R01 HD 094378, R01 HD 094380, R01 HD 10036701, U54 MD 007602) and hold a patent for methods for novel diagnostics and therapeutics for uterine sarcoma (US Pat No. 9,790,562 B2). Andrea Lukes received research support from AbbVie, Astellas, Bayer, Ferring, Merck, Mithra, Mylan, Myovant Sciences, Organon. They have been a consultant for AbbVie and Myovant Sciences and served on the Speaker Bureau for AbbVie. Served on the advisory board for BCD Meetings & Events (December 10, 2021).Roberta Venturella has been a consultant for IBSA Pharmaceuticals and Myovant Sciences Inc. Elizabeth Stewart has been a consultant for AbbVie, Bayer, Myovant Sciences, and ObsEva. She received Research Support from the National Institutes of Health (R01 HD105714) and AHRQ and PCORI (P50 HS023418). She holds a patent for Methods and Compounds for Treatment of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (US 6440445), which has no commercial activity. She has received royalties from UpToDate and payments for the development of educational content from the Med Learning Group, PER, Massachusetts Medical Society, and Peer View. Laura McKain is a former Myovant Sciences, Inc. employee. She served on the speaker's bureau and recently as consultant. She received payment from Evofem Biosciences (consultant role) and Cooper Surgical (consultant role). She is a Myovant Sciences shareholder. Rachel Wagman and Li are current employees of Myovant Sciences, Inc. Alfred Poindexter and Claudio Villarroel did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Antagonists Revolutionizing Gynecology.Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Dec 1;140(6):917-919. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000005012. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 36357969 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

