Outstanding Enrofloxacin Removal Using an Unmodified Low-Cost Sorbent Prepared from the Leaves of Pyracantha koidzumii
- PMID: 36358218
- PMCID: PMC9686792
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11111563
Outstanding Enrofloxacin Removal Using an Unmodified Low-Cost Sorbent Prepared from the Leaves of Pyracantha koidzumii
Abstract
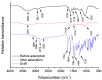
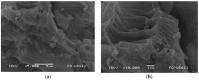
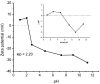
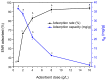
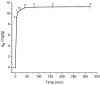
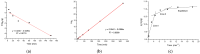
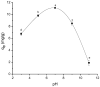
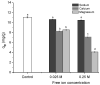
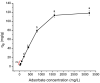
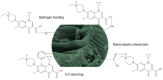
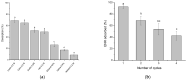
Increasing discharges of synthetic antimicrobial agents from industrial and municipal sewage, as well as from agricultural runoffs into water bodies, is still a global challenge. Here, an unmodified low-cost sorbent was prepared in an ecofriendly manner from Pyracantha koidzumii leaves for the removal of enrofloxacin (ENR). Sorbent characterization was accomplished using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), BET surface area, zeta potential, and point of zero charge. Biosorption assays were carried out via batch mode concerning the impact of adsorbent dosage, contact time, solution pH, solution ionic strength, adsorbate concentration, and temperature. In general, ENR adsorption was significantly correlated with pH and ionic strength. At a neutral pH, the sorbent had a theoretical maximal ENR uptake of 138.89 mg/g. However, the adsorption capacity was significantly affected by the presence of high concentrations of divalent cations (Ca2+ and Mg2+). The findings from the kinetics and isotherms showed that the pseudo-second-order kinetic and Langmuir isotherm models best fit the experimental data. Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and π-π stacking were the most important mechanisms of adsorption of ENR onto the P. koidzumii sorbent. Overall, this study suggests the promising application of this agricultural residue for the efficient removal of ENR from water.
Keywords: adsorption; agro-waste-based sorbent; aqueous media; enrofloxacin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biosorption of B-aflatoxins Using Biomasses Obtained from Formosa Firethorn [Pyracantha koidzumii (Hayata) Rehder].Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jul 13;8(7):218. doi: 10.3390/toxins8070218. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27420096 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Removal of Toxic Remazol Brilliant Blue-R Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Juglans nigra Shell Biomass Activated Carbon as Potential Adsorbent: Optimization, Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Investigation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;23(20):12484. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012484. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293336 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of graphene oxide/inulin impregnated with ZnO nanoparticles for efficient removal of enrofloxacin from water: Taguchi-optimized experimental analysis.J Environ Manage. 2022 Sep 15;318:115525. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115525. Epub 2022 Jun 17. J Environ Manage. 2022. PMID: 35724574
-
A novel approach to preparation of nano-adsorbent from agricultural wastes (Saccharum officinarum leaves) and its environmental application.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Feb;26(6):5305-5314. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3734-z. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30446914
-
Preparation and characterization of a novel polyethyleneimine cation-modified persimmon tannin bioadsorbent for anionic dye adsorption.J Environ Manage. 2018 Jul 1;217:305-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.107. Epub 2018 Apr 5. J Environ Manage. 2018. PMID: 29614479 Review.
References
-
- Focazio M.J., Kolpin D.W., Barnes K.K., Furlong E.T., Meyer M.T., Zaugg S.D., Barber L.B., Thurman M.E. A national reconnaissance for pharmaceuticals and other organic wastewater contaminants in the United States—II) Untreated drinking water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2008;402:201–216. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.02.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Viana P., Meisel L., Lopes A., De Jesus R., Sarmento G., Duarte S., Sepodes B., Fernandes A., Dos Santos M.M.C., Almeida A., et al. Identification of Antibiotics in Surface-Groundwater. A Tool towards the Ecopharmacovigilance Approach: A Portuguese Case-Study. Antibiotics. 2021;10:888. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080888. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

