An Optimization of Oregano, Thyme, and Lemongrass Essential Oil Blend to Simultaneous Inactivation of Relevant Foodborne Pathogens by Simplex-Centroid Mixture Design
- PMID: 36358227
- PMCID: PMC9686886
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11111572
An Optimization of Oregano, Thyme, and Lemongrass Essential Oil Blend to Simultaneous Inactivation of Relevant Foodborne Pathogens by Simplex-Centroid Mixture Design
Abstract
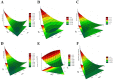
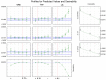
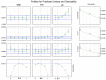
(1) Background: This study aimed to use the simplex-centroid mixture design methodology coupled with a microdilution assay to predict optimal essential oil (EO) formulations against three potential foodborne pathogens simultaneously through the desirability (D) function. (2) Methods: Oregano (ORE; Origanum vulgare), thyme (THY; Thymus vulgaris), and lemongrass (LG; Cymbopogon citratus) and their blends were evaluated concerning minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) for Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. (3) Results: THY combined with ORE or LG were the most promising EO formulations in inhibiting and killing each bacterium separately. Regarding the simultaneous effect, the optimal proportion for maximum inhibition was composed of 75% ORE, 15% THY, and 10% LG, while for maximum inactivation was 50% ORE, 40% THY, and 10% LG. (4) Conclusion: The multiresponse optimization allowed identifying an EO blend to simultaneously control three potential foodborne pathogens. This first report could be a helpful natural and green alternative for the industry to produce safer food products and mitigate public health risks.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; desirability function; minimum bactericidal concentration; minimum inhibitory concentration; natural antimicrobials; volatile oils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest and no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pateiro M., Munekata P.E.S., Sant’Ana A.S., Domínguez R., Rodríguez-Lázaro D., Lorenzo J.M. Application of essential oils as antimicrobial agents against spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021;337:108966. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108966. - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO Draft Who Global Strategy for Food Safety 2022–2030. [(accessed on 30 October 2022)]. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/food-safety/public-consult....
-
- WHO Food Safety. [(accessed on 29 October 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety.
-
- FDA Outbreaks of Foodborne Illness. [(accessed on 30 October 2022)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/recalls-outbreaks-emergencies/outbreaks-foodbor....
Grants and funding
- [E-26/200.891/2021], [E-26/010.000148/2020], and [E-26/201.790/2020]/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- [313119/2020-1], [402215/2022-2] and [200468/2022-7]/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- [88887.518752/2020-00]/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

