Differential Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder: Genetic and Hormonal Assessment and the Influence of Early-Life Stress
- PMID: 36358401
- PMCID: PMC9688727
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12111476
Differential Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder: Genetic and Hormonal Assessment and the Influence of Early-Life Stress
Abstract
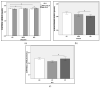
Few studies have assessed biomarkers for the differentiation of major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD). However, some elements of depression such as hormones and receptors of the renin-angiotensin-adrenal system (RAAS), the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and history of early-life stress (ELS) could be considered for differential diagnosis. Therefore, this study aimed to assess aldosterone and cortisol levels, MR and GR gene polymorphisms, and ELS as potential biomarkers for differentiating MDD and BD. This study presents a case-control design. Groups comprised samples for genetic, cortisol, and aldosterone analysis: healthy control (HC; n = 113/97/103), MDD (n = 78/69/67) and BD (n = 82/68/65) subjects. Furthermore, all subjects were assessed for diagnostic screening, the severity of depression, and history of ELS by applying MINI-PLUS, GRID-HDRS, and CTQ, respectively. In addition, genotype and allelic frequencies of GR (N363S, R22/23K and BclI) and MR (MI180V and -2G/C) polymorphisms were evaluated via PCR. Our findings demonstrate that basal aldosterone levels may be a biomarker for differentiating BD and MDD. Furthermore, ELS affects the HPA axis in BD, cortisol may be considered a biomarker for distinguishing BD and MDD, but only in the absence of ELS, and, finally, history of ELS and MR-2G/C variant alleles are factors that contribute to the severity of depressive symptoms in MDD and BD.
Keywords: aldosterone; biomarker; bipolar; cortisol; depression; early-life stress (ELS); glucocorticoid receptor (GR); mineralocorticoid receptor (MR); polymorphism (SNP).
Conflict of interest statement
MF Juruena is an independent researcher funded by the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre (BRC)at the South London and Maudsley (SLaM) NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London and received honoraria for lectures and advisory boards from most of the major pharmaceutical companies with drugs used in affective and related disorders. The views expressed in this paper belong to the authors and not necessarily to the NHS, NIHR, or the Department of Health. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 2013. (DSM-5)
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA3.0 IGO.
-
- Mari J.J., Pitta J.C.N. Psiquiatria por Meio de Casos Clínicos. Editora Manole; São Paulo, Brazil: 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

