Multiple Machine Learning Approaches for Morphometric Parameters in Prediction of Hydrocephalus
- PMID: 36358410
- PMCID: PMC9688126
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12111484
Multiple Machine Learning Approaches for Morphometric Parameters in Prediction of Hydrocephalus
Abstract
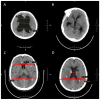
Background: The diagnosis of hydrocephalus is mainly based on imaging findings. However, the significance of many imaging indicators may change, especially in some degenerative diseases, and even lead to misdiagnosis.
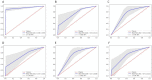
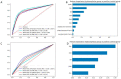
Methods: This study explored the effectiveness of commonly used morphological parameters and typical radiographic findings in hydrocephalus diagnosis. The patients' imaging data were divided into three groups, including the hydrocephalus group, the symptomatic group, and the normal control group. The diagnostic validity and weight of various parameters were compared between groups by multiple machine learning methods.
Results: Our results demonstrated that Evans' ratio is the most valuable diagnostic indicator compared to the hydrocephalus group and the normal control group. But frontal horns' ratio is more useful in diagnosing patients with symptoms. Meanwhile, the sign of disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space and third ventricle enlargement could be effective diagnostic indicators in all situations.
Conclusion: Both morphometric parameters and radiological features were essential in diagnosing hydrocephalus, but the weights are different in different situations. The machine learning approaches can be applied to optimize the diagnosis of other diseases and consistently update the clinical diagnostic criteria.
Keywords: hydrocephalus; imaging diagnosis; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pisapia J.M., Rozycki M., Akbari H., Bakas S., Thawani J.P., Moldenhauer J.S., Storm P.B., Zarnow D.M., Davatzikos C., Heuer G.G. Correlations of atrial diameter and frontooccipital horn ratio with ventricle size in fetal ventriculomegaly. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017;19:300–306. doi: 10.3171/2016.9.PEDS16210. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

