Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning Classification of Resting-State EEG Microstates in Schizophrenia: A Proof-of-Concept Preliminary Study Based on Secondary Analysis
- PMID: 36358423
- PMCID: PMC9688063
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12111497
Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning Classification of Resting-State EEG Microstates in Schizophrenia: A Proof-of-Concept Preliminary Study Based on Secondary Analysis
Abstract
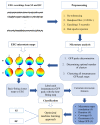
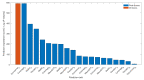
Resting-state electroencephalography (EEG) microstates reflect sub-second, quasi-stable states of brain activity. Several studies have reported alterations of microstate features in patients with schizophrenia (SZ). Based on these findings, it has been suggested that microstates may represent neurophysiological biomarkers for the classification of SZ. To explore this possibility, machine learning approaches can be employed. Bayesian optimization is a machine learning approach that selects the best-fitted machine learning model with tuned hyperparameters from existing models to improve the classification. In this proof-of-concept preliminary study based on secondary analysis, 20 microstate features were extracted from 14 SZ patients and 14 healthy controls' EEG signals. These parameters were then ranked as predictors based on their importance, and an optimized machine learning approach was applied to evaluate the performance of the classification. SZ patients had altered microstate features compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, Bayesian optimization outperformed conventional multivariate analyses and showed the highest accuracy (90.93%), AUC (0.90), sensitivity (91.37%), and specificity (90.48%), with reliable results using just six microstate predictors. Altogether, in this proof-of-concept study, we showed that machine learning with Bayesian optimization can be utilized to characterize EEG microstate alterations and contribute to the classification of SZ patients.
Keywords: microstate analysis; microstate map correlation; optimized machine learning; resting-state EEG; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
EEG microstate features for schizophrenia classification.PLoS One. 2021 May 14;16(5):e0251842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251842. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33989352 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate patterns of EEG microstate parameters and their role in the discrimination of patients with schizophrenia from healthy controls.Psychiatry Res. 2020 Jun;288:112938. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112938. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Psychiatry Res. 2020. PMID: 32315875
-
Resting-state connectivity in the prodromal phase of schizophrenia: insights from EEG microstates.Schizophr Res. 2014 Feb;152(2-3):513-20. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.12.008. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Schizophr Res. 2014. PMID: 24389056
-
Machine learning detects EEG microstate alterations in patients living with temporal lobe epilepsy.Seizure. 2018 Oct;61:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2018.07.007. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Seizure. 2018. PMID: 30044996 Review.
-
Microstates in resting-state EEG: current status and future directions.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Feb;49:105-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.010. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25526823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resting-state EEG microstate features for Alzheimer's disease classification.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 12;19(12):e0311958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311958. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39666689 Free PMC article.
-
Microstate D as a Biomarker in Schizophrenia: Insights from Brain State Transitions.Brain Sci. 2024 Sep 28;14(10):985. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14100985. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39451999 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of optimized machine learning approach to the understanding of medial tibial stress syndrome in male military personnel.BMC Res Notes. 2023 Jun 29;16(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13104-023-06404-0. BMC Res Notes. 2023. PMID: 37386606 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia diagnosis based on diverse epoch size resting-state EEG using machine learning.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Aug 20;10:e2170. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2170. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39314693 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of EEG based automated schizophrenia classification through machine learning and deep learning.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Feb 14;18:1347082. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1347082. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38419961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bleuler E. Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias. International Universities Press; New York, NY, USA: 1950.
-
- Kraepelin E. In: Dementia Praecox and Paraphrenia. Barclay R.M., translator. Krieger; Huntingdon, NY, USA: 1919.
-
- Vignapiano A., Koenig T., Mucci A., Giordano G.M., Amodio A., Altamura M., Bellomo A., Brugnoli R., Corrivetti G., Di Lorenzo G. Disorganization and cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: New insights from electrophysiological findings. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019;145:99–108. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2019.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

