Possible Effects and Mechanisms of Dietary Natural Products and Nutrients on Depression and Anxiety: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 36358502
- PMCID: PMC9686692
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11112132
Possible Effects and Mechanisms of Dietary Natural Products and Nutrients on Depression and Anxiety: A Narrative Review
Abstract
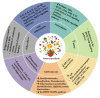
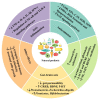
Depression and anxiety are severe public health problems and have attracted more and more attention from researchers of food science and nutrition. Dietary natural products and nutrients, such as fish, coffee, tea, n-3 PUFA, lycopene, and dietary fiber, could play a vital role in the prevention and management of these diseases. The potential mechanisms of action mainly include inhibiting inflammation, ameliorating oxidative stress, modulating the microbiota-gut-brain axis, suppressing hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hyperactivity, and regulating the levels of monoamine neurotransmitters. In this narrative review, we summarize the most recent advancements regarding the effects of dietary natural products and nutrients on depression and anxiety, and their underlying mechanisms are discussed. We hope that this paper can provide a better understanding of the anti-depressive and anxiolytic action of dietary natural products, and that it is also helpful for developing dietary natural products for functional food, dietary supplements, or auxiliary agents for the prevention and management of these diseases.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; dietary natural products; gut microbiota; nutrients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutritional Modulation of the Gut-Brain Axis: A Comprehensive Review of Dietary Interventions in Depression and Anxiety Management.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 14;14(10):549. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100549. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Polyphenol Supplementation in Preventing and Managing Depression: A Review of Current Research.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;14(10):1342. doi: 10.3390/life14101342. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fermented foods, the gut and mental health: a mechanistic overview with implications for depression and anxiety.Nutr Neurosci. 2020 Sep;23(9):659-671. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2018.1544332. Epub 2018 Nov 11. Nutr Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 30415609 Review.
-
Targeting Gut Microbiota for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes Mellitus by Dietary Natural Products.Foods. 2019 Sep 25;8(10):440. doi: 10.3390/foods8100440. Foods. 2019. PMID: 31557941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut-Microbiota-Brain Axis and Its Effect on Neuropsychiatric Disorders With Suspected Immune Dysregulation.Clin Ther. 2015 May 1;37(5):984-95. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.04.002. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 26046241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional Modulation of the Gut-Brain Axis: A Comprehensive Review of Dietary Interventions in Depression and Anxiety Management.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 14;14(10):549. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100549. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Gut-Microbiome and mental health and effects of probiotics on psychiatric disorders: A Meta-analysis and systematic review.Niger Med J. 2025 Apr 3;66(1):13-25. doi: 10.71480/nmj.v66i1.601. eCollection 2025 Jan-Feb. Niger Med J. 2025. PMID: 40309529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Administration of Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium Offers Enhanced Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activity in a Dose Dependent Manner.Brain Behav. 2025 May;15(5):e70564. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70564. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40384043 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical Activities of Theanine: A Phytochemical Nutrient.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Aug 13;13(8):e70811. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70811. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40822528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonols in Action: Targeting Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6888. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086888. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108052 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferrari A.J., Santomauro D.F., Herrera A.M.M., Shadid J., Ashbaugh C., Erskine H.E., Charlson F.J., Degenhardt L., Scott J.G., McGrath J.J., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022;9:137–150. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00395-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruno A., Dolcetti E., Rizzo F.R., Fresegna D., Musella A., Gentile A., De Vito F., Caioli S., Guadalupi L., Bullitta S., et al. Inflammation-associated synaptic alterations as shared threads in depression and multiple sclerosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020;14:169. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00169. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

