Quercetin Abates Aluminum Trioxide Nanoparticles and Lead Acetate Induced Altered Sperm Quality, Testicular Oxidative Damage, and Sexual Hormones Disruption in Male Rats
- PMID: 36358505
- PMCID: PMC9686927
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11112133
Quercetin Abates Aluminum Trioxide Nanoparticles and Lead Acetate Induced Altered Sperm Quality, Testicular Oxidative Damage, and Sexual Hormones Disruption in Male Rats
Abstract
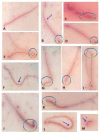
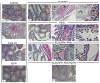
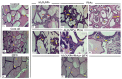
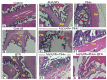
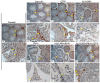
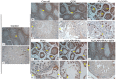
This study examined the effects of exposure to lead acetate (PbAc) and/or aluminum trioxide nanoparticles (Al2O3NPs) on testicular function. Additionally, the probable reproprotective effects of quercetin (QTN) against Al2O3NPs and PbAc co-exposure in male Sprague Dawely rats were assessed. Al2O3NPs (100 mg/kg b.wt.), PbAc (50 mg/kg b.wt.), and QTN (20 mg/kg b.wt.) were orally administered for 60 days. Then, spermiogram, histopathological examinations of the testis and accessory glands, and immunohistochemical detection of androgen receptors (AR) and tumor necrotic factor alpha (TNF-α) were achieved. Moreover, serum levels of male sex hormones and testicular levels of antioxidant indices were estimated. The results showed that Al2O3NPs and/or PbAc caused significant sperm abnormalities, testicular oxidative stress, and histopathological changes. Furthermore, serum testosterone, LH, and FSH levels significantly decreased, while estradiol levels significantly increased. The Al2O3NPs and/or PbAc co-exposed group had more obvious disturbances. Furthermore, QTN co-administration significantly reversed the Al2O3NPs and PbAc-induced testicular histopathological alterations, reduced antioxidant defenses, and altered AR and TNF-α immune expression in testicular tissues. Conclusively, Al2O3NPs and/or PbAc evoked testicular dysfunction by inducing oxidative injury and inflammation. However, QTN oral dosing effectively mitigated the negative effects of Al2O3NPs and PbAc by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation and improving the antioxidant defense system.
Keywords: aluminum trioxide nanoparticles; androgen receptors; inflammation; lead acetate; oxidative stress; quercetin; rats; tumor necrotic factor alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ameliorative effects of quercetin against hepatic toxicity of oral sub-chronic co-exposure to aluminum oxide nanoparticles and lead-acetate in male rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;396(4):737-747. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02351-y. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36472630 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of syringic acid on oxidative stress, autophagy, apoptosis, inflammation pathways against testicular damage induced by lead acetate.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2023 Dec;80:127315. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127315. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37801787
-
Thymoquinone attenuates testicular and spermotoxicity following subchronic lead exposure in male rats: Possible mechanisms are involved.Life Sci. 2019 Aug 1;230:132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.067. Epub 2019 May 25. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31136753
-
Effects of sinapic acid on lead acetate-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation in testicular tissue.Environ Toxicol. 2023 Nov;38(11):2656-2667. doi: 10.1002/tox.23900. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Environ Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37471654
-
Chrysin protects against testicular toxicity caused by lead acetate in rats with its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties.J Food Biochem. 2021 Feb;45(2):e13593. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13593. Epub 2020 Dec 27. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33368351
Cited by
-
Restorative effects of gallic acid against sub-chronic hepatic toxicity of co-exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles and arsenic trioxide in male rats.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 15;9(6):e17326. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17326. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37389053 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone effects on autophagy, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in cisplatin-induced testicular damage in mice.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Jul;41(7):1881-1891. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03097-7. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 38568464 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin as a Promising Agent for Enhancing Female Reproductive Function and Treating Associated Disorders.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 21;12(10):2405. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102405. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Activity of Flavonoid Quercetin and Its Therapeutic Potential in Testicular Injury.Nutrients. 2023 May 8;15(9):2231. doi: 10.3390/nu15092231. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of heat-killed Lactobacillus reuteri against bile acid-induced male reproductive toxicity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 15. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04092-0. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40232374
References
-
- Hamdi H. Testicular dysfunction induced by aluminum oxide nanoparticle administration in albino rats and the possible protective role of the pumpkin seed oil. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2020;81:42. doi: 10.1186/s41936-020-00178-8. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

