The Role of the Thioredoxin System in Brain Diseases
- PMID: 36358532
- PMCID: PMC9686621
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11112161
The Role of the Thioredoxin System in Brain Diseases
Abstract
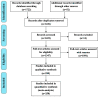
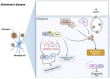
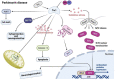
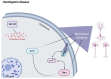
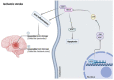
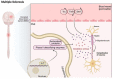
The thioredoxin system, consisting of thioredoxin (Trx), thioredoxin reductase (TrxR), and NADPH, plays a fundamental role in the control of antioxidant defenses, cell proliferation, redox states, and apoptosis. Aberrations in the Trx system may lead to increased oxidative stress toxicity and neurodegenerative processes. This study reviews the role of the Trx system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases, brain stroke, and multiple sclerosis. Trx system plays an important role in the pathophysiology of those disorders via multiple interactions through oxidative stress, apoptotic, neuro-immune, and pro-survival pathways. Multiple aberrations in Trx and TrxR systems related to other redox systems and their multiple reciprocal relationships with the neurodegenerative, neuro-inflammatory, and neuro-oxidative pathways are here analyzed. Genetic and environmental factors (nutrition, metals, and toxins) may impact the function of the Trx system, thereby contributing to neuropsychiatric disease. Aberrations in the Trx and TrxR systems could be a promising drug target to prevent and treat neurodegenerative, neuro-inflammatory, neuro-oxidative stress processes, and related brain disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; antioxidants; metals; multiple sclerosis; oxidative stress; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The thioredoxin antioxidant system.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 23899494 Review.
-
A thioredoxin reductase and/or thioredoxin system-based mechanism for antioxidant effects of ambroxol.Biochimie. 2014 Feb;97:92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.09.024. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 24103200
-
The Thioredoxin System of Mammalian Cells and Its Modulators.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 21;10(7):1757. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071757. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain mitochondria from DJ-1 knockout mice show increased respiration-dependent hydrogen peroxide consumption.Redox Biol. 2014 Apr 24;2:667-72. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.04.010. eCollection 2014. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 24936441 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme-linked immunospot assay for detection of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase secretion from cells.Methods Enzymol. 2002;353:22-35. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(02)53033-0. Methods Enzymol. 2002. PMID: 12078496
Cited by
-
Auranofin Modulates Thioredoxin Reductase/Nrf2 Signaling in Peripheral Immune Cells and the CNS in a Mouse Model of Relapsing-Remitting EAE.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 10;11(9):2502. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092502. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760943 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Patch-Clamp/Proteomics of Human Alzheimer's Disease iPSC-Derived Excitatory Neurons Versus Isogenic Wild-Type Controls Suggests Novel Causation and Therapeutic Targets.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(29):e2400545. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400545. Epub 2024 May 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38773714 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative, antimigratory, and apoptotic effects of diffractaic and vulpinic acids as thioredoxin reductase 1 inhibitors on cervical cancer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;397(3):1525-1535. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02698-w. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37658214
-
Disruption of Bacterial Thiol-Dependent Redox Homeostasis by Magnolol and Honokiol as an Antibacterial Strategy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 30;12(6):1180. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061180. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371909 Free PMC article.
-
Icaritin greatly attenuates β-amyloid-induced toxicity in vivo.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14527. doi: 10.1111/cns.14527. Epub 2023 Nov 21. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37990437 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

