Is Lymphocyte C-Reactive Protein Ratio Useful for Predicting Survival in Patients with Non-Metastatic Soft Tissue Sarcoma?
- PMID: 36358634
- PMCID: PMC9655955
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14215214
Is Lymphocyte C-Reactive Protein Ratio Useful for Predicting Survival in Patients with Non-Metastatic Soft Tissue Sarcoma?
Abstract
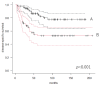
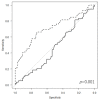
Background: Recently, the lymphocyte-to-CRP ratio (LCR) was found to have a prognostic role in many cancers. However, the clinical significance of LCR in patients with soft tissue sarcoma (STS) has not yet been established. This study aimed to determine whether LCR can predict disease-specific survival (DSS) and event-free survival (EFS) in patients with STS. Methods: In this study, 132 patients were enrolled. The mean follow-up periods were 76.5 months. Blood examinations were performed prior to treatment for all patients. Results: The 5-year DSS in patients with higher and lower LCR was 86.5% and 52.8%, respectively (p < 0.001). Patients with lower LCR had worse survival than those with higher LCR. The 5-year EFS in patients with higher and lower LCR was 66.2% and 31.2%, respectively (p < 0.001). On Receiver operating characteristic analysis, however, there was no significant difference in the area under curve (AUC) between CRP level (AUC = 0.72) and LCR (AUC = 0.711). Conclusions: LCR may be a prognostic factor for predicting oncological events in multivariate analysis, although ROC analysis could not show the superiority of LCR to CRP for predicting oncological outcomes in patients with STS.
Keywords: lymphocyte- to- C-reactive protein ratio; soft tissue sarcoma; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nakamura T., Asanuma K., Takao M., Yamanaka T., Koike H., Chen-Yoshikawa T.F., Tsukushi S., Kuroda H., Kozawa E., Sano M., et al. Clinical Outcome in Soft Tissue Sarcoma Patients with Lung Metastasis Who Received Metastasectomy and/or Radiofrequency Ablation: Tokai Musculoskeletal Oncology Consortium Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021;13:8473–8480. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S333721. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

