Neural Component of the Tumor Microenvironment in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36358664
- PMCID: PMC9657005
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14215246
Neural Component of the Tumor Microenvironment in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
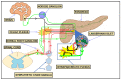
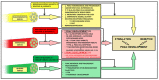
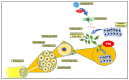
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly aggressive primary malignancy of the pancreas, with a dismal prognosis and limited treatment options. It possesses a unique tumor microenvironment (TME), generating dense stroma with complex elements cross-talking with each other to promote tumor growth and progression. Diversified neural components makes for not having a full understanding of their influence on its aggressive behavior. The aim of the study was to summarize and integrate the role of nerves in the pancreatic tumor microenvironment. The role of autonomic nerve fibers on PDAC development has been recently studied, which resulted in considering the targeting of sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways as a novel treatment opportunity. Perineural invasion (PNI) is commonly found in PDAC. As the severity of the PNI correlates with a poorer prognosis, new quantification of this phenomenon, distinguishing between perineural and endoneural invasion, could feature in routine pathological examination. The concepts of cancer-related neurogenesis and axonogenesis in PDAC are understudied; so, further research in this field may be warranted. A better understanding of the interdependence between the neural component and cancer cells in the PDAC microenvironment could bring new nerve-oriented treatment options into clinical practice and improve outcomes in patients with pancreatic cancer. In this review, we aim to summarize and integrate the current state of knowledge and future challenges concerning nerve-cancer interactions in PDAC.
Keywords: pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; perineural invasion; tumor innervation; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the Cancer-Neuronal Crosstalk in the Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 8;24(19):14989. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914989. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Novel Mechanisms Involved in Perineural Invasion in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 1;17(5):852. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050852. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075699 Free PMC article.
-
Hallmarks of perineural invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: new biological dimensions.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 25;14:1421067. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1421067. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39119085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of perineural invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Aug;41(8):642-660. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12188. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34264020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk Between Peripheral Innervation and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Neurosci Bull. 2023 Nov;39(11):1717-1731. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01082-1. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Neurosci Bull. 2023. PMID: 37347365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the role of nerves in head and neck cancers - a review.Oncol Rev. 2025 Jan 20;18:1514004. doi: 10.3389/or.2024.1514004. eCollection 2024. Oncol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39906323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Cancer-Neuronal Crosstalk in the Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 8;24(19):14989. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914989. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane Lipid Derivatives: Roles of Arachidonic Acid and Its Metabolites in Pancreatic Physiology and Pathophysiology.Molecules. 2023 May 24;28(11):4316. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114316. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Crosstalk between Nerves and Cancer-A Poorly Understood Phenomenon and New Possibilities.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 15;16(10):1875. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101875. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Evaluation of the Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment: Opportunities and Challenges.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 15;16(4):794. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040794. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

