The Predictive and Prognostic Role of RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK Pathway Alterations in Breast Cancer: Revision of the Literature and Comparison with the Analysis of Cancer Genomic Datasets
- PMID: 36358725
- PMCID: PMC9653766
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14215306
The Predictive and Prognostic Role of RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK Pathway Alterations in Breast Cancer: Revision of the Literature and Comparison with the Analysis of Cancer Genomic Datasets
Abstract
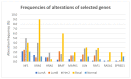
Although gene alterations of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway are uncommon in breast cancer, this pathway is frequently activated in breast tumors, implying its role in tumor progression. We describe, after a revision of the literature, the frequency and types of gene alterations affecting this pathway in breast cancer by analyzing some public datasets from cBioPortal. Moreover, we consider their prognostic and predictive impact on treatment response, along with the role of transcriptomic predictors of RAS pathway activation. Our analysis shows that the driver alterations in RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway-related genes are detected in 11% of primary breast cancers. The most frequently mutated genes are NF1 and KRAS, while copy number alterations mainly affect KRAS and BRAF, especially in basal-like tumors. The subgroup of patients carrying these alterations shows a worse prognosis; alterations in NF1 and RAF1 are associated with significantly reduced breast-cancer-specific survival in multivariate analysis. The literature review shows that the pathway is implicated, either by genetic or epigenetic alterations or by signaling network adaptations, in the mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to a wide range of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer. A thorough understanding of these alterations is critical for developing combination therapies that can delay or overcome drug resistance.
Keywords: ERK cascade; MAPK; RAS pathway; breast cancer; genomic alterations; predictive impact; prognostic impact.
Conflict of interest statement
AR participated in advisory boards of Novartis, Roche, and Pfizer and received payment for travel and conference expenses from Gilead. DG participated in advisory boards of Novartis, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Istituto Gentili, Roche.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationships among KRAS mutation status, expression of RAS pathway signaling molecules, and clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb 21;25(7):808-823. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.808. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30809081 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of NF1 in cutaneous melanoma is associated with RAS activation and MEK dependence.Cancer Res. 2014 Apr 15;74(8):2340-50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2625. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24576830 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Acquired Resistance to RAF Inhibitor Combinations in BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Pathway Alterations.Cancer Discov. 2015 Apr;5(4):358-67. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1518. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 25673644 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive pancancer genomic analysis reveals (RTK)-RAS-RAF-MEK as a key dysregulated pathway in cancer: Its clinical implications.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Feb;54:14-28. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 29175106 Review.
-
Onco-immunomodulatory properties of pharmacological interference with RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway hyperactivation.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 27;12:931774. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.931774. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35965494 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions between hedgehog signaling pathway and the complex tumor microenvironment in breast cancer: current knowledge and therapeutic promises.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 9;22(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01812-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39252010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: mechanisms and role in endocrine resistance.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 8;14:1406951. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1406951. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39040443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 23;15(19):4689. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194689. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Breast Cancer: The Familiar, the Emerging, and the Uncharted Territories.Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 25;13(9):1306. doi: 10.3390/biom13091306. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive advances in HER2-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer: unveiling molecular mechanisms and exploring cutting-edge targeted therapies for enhanced patient outcomes.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 29. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04204-w. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40439885 Review.
References
-
- Johnson C., Burkhart D.L., Haigis K.M. Classification of KRAS-Activating Mutations and the Implications for Therapeutic Intervention. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:913–923. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

