Glucose Enhances Pro-Tumorigenic Functions of Mammary Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells on Breast Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 36358839
- PMCID: PMC9655059
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14215421
Glucose Enhances Pro-Tumorigenic Functions of Mammary Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells on Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
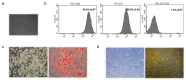
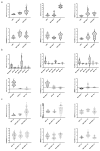
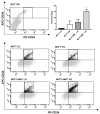
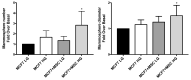
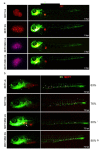
Adiposity and diabetes affect breast cancer (BC) progression. We addressed whether glucose may affect the interaction between mammary adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MAT-MSCs) and BC cells. Two-dimensional co-cultures and spheroids were established in 25 mM or 5.5 mM glucose (High Glucose-HG or Low Glucose-LG) by using MAT-MSCs and MCF7 or MDA-MB231 BC cells. Gene expression was measured by qPCR, while protein levels were measured by cytofluorimetry and ELISA. CD44high/CD24low BC stem-like sub-population was quantified by cytofluorimetry. An in vivo zebrafish model was assessed by injecting spheroid-derived labeled cells. MAT-MSCs co-cultured with BC cells showed an inflammatory/senescent phenotype with increased abundance of IL-6, IL-8, VEGF and p16INK4a, accompanied by altered levels of CDKN2A and LMNB1. BC cells reduced multipotency and increased fibrotic features modulating OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, αSMA and FAP in MAT-MSCs. Of note, these co-culture-mediated changes in MAT-MSCs were partially reverted in LG. Only in HG, MAT-MSCs increased CD44high/CD24low MCF7 sub-population and promoted their ability to form mammospheres. Injection in zebrafish embryos of HG spheroid-derived MCF7 and MAT-MSCs was followed by a significant cellular migration and caudal dissemination. Thus, MAT-MSCs enhance the aggressiveness of BC cells in a HG environment.
Keywords: breast cancer; glucose; mammary adipose tissue; mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

