Nanoparticle Enhancement of Natural Killer (NK) Cell-Based Immunotherapy
- PMID: 36358857
- PMCID: PMC9653801
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14215438
Nanoparticle Enhancement of Natural Killer (NK) Cell-Based Immunotherapy
Abstract
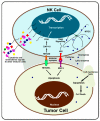
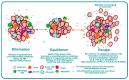
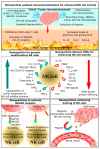
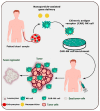
Natural killer (NK) cells are one of the first lines of defense against infections and malignancies. NK cell-based immunotherapies are emerging as an alternative to T cell-based immunotherapies. Preclinical and clinical studies of NK cell-based immunotherapies have given promising results in the past few decades for hematologic malignancies. Despite these achievements, NK cell-based immunotherapies have limitations, such as limited performance/low therapeutic efficiency in solid tumors, the short lifespan of NK cells, limited specificity of adoptive transfer and genetic modification, NK cell rejection by the patient's immune system, insignificant infiltration of NK cells into the tumor microenvironment (TME), and the expensive nature of the treatment. Nanotechnology could potentially assist with the activation, proliferation, near-real time imaging, and enhancement of NK cell cytotoxic activity by guiding their function, analyzing their performance in near-real time, and improving immunotherapeutic efficiency. This paper reviews the role of NK cells, their mechanism of action in killing tumor cells, and the receptors which could serve as potential targets for signaling. Specifically, we have reviewed five different areas of nanotechnology that could enhance immunotherapy efficiency: nanoparticle-assisted immunomodulation to enhance NK cell activity, nanoparticles enhancing homing of NK cells, nanoparticle delivery of RNAi to enhance NK cell activity, genetic modulation of NK cells based on nanoparticles, and nanoparticle activation of NKG2D, which is the master regulator of all NK cell responses.
Keywords: NK cell receptors; NK cell-mediated immunotherapy; NK cells; applications of nanoparticles; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent Advances to Augment NK Cell Cancer Immunotherapy Using Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Apr 9;13(4):525. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040525. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33918941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral and Nonviral Engineering of Natural Killer Cells as Emerging Adoptive Cancer Immunotherapies.J Immunol Res. 2018 Sep 17;2018:4054815. doi: 10.1155/2018/4054815. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30306093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of intrinsic inhibitory checkpoints using nano-carriers to unleash NK cell activity.EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Jan 11;14(1):e14073. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114073. Epub 2021 Nov 2. EMBO Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34725941 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Resistance to Natural Killer Cell Based Immunotherapies for Solid Tumors.Front Oncol. 2019 Feb 11;9:51. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00051. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30805309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered nanoparticles to enhance natural killer cell activity towards onco-immunotherapy: a review.Arch Pharm Res. 2020 Jan;43(1):32-45. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01218-1. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Arch Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 31993969 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Applications of Nanomedicine: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives.Molecules. 2024 Apr 30;29(9):2073. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092073. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAR-NK Cell Therapy: A Transformative Approach to Overcoming Oncological Challenges.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 20;14(8):1035. doi: 10.3390/biom14081035. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in research on immune escape mechanism of glioma.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Jul;29(7):1709-1720. doi: 10.1111/cns.14217. Epub 2023 Apr 23. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 37088950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor-natural killer (CAR-NK) cell immunotherapy: A bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2023.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2415187. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2415187. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39414236 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted intervention in obesity-associated atrial fibrosis using nanoparticle-loaded fusion protein.Apoptosis. 2025 Jun;30(5-6):1547-1571. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02104-1. Epub 2025 Apr 26. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40281309
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

