Recurrence of Oral Leukoplakia after CO2 Laser Resection: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 36358873
- PMCID: PMC9658806
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14215455
Recurrence of Oral Leukoplakia after CO2 Laser Resection: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study is to assess the efficacy of CO2 laser treatment in oral leukoplakia and to analyse the recurrence rate of oral leukoplakia lesions at 18-month follow-up.
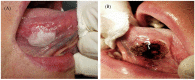
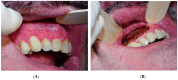
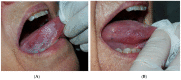
Materials and methods: A prospective clinical study regarding CO2 laser treatment for oral leukoplakia was conducted, in which 39 patients with a total of 53 oral leukoplakias were included. Follow-up was performed at 18 months post-surgery and the following variables were studied: sex, age, associated risk factors, clinical classification, size, location and presence of epithelial dysplasia, recurrence, and rate of malignant transformation after resection.
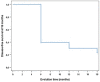
Results: In the analysis of the final results 18 months after baseline, a treatment success rate of 43.75% was observed. Oral leukoplakia recurred in 54.17% of cases, and 2.08% of leukoplakias progressed to cancer. Among all the studied variables (age, tobacco use, size, location, clinical type or histology), no significant differences were found with regard to recurrence.
Conclusion: The use of CO2 laser therapy to treat leukoplakia lesions is sufficient to remove such lesions. However, parameters that can assess recurrence need to be sought.
Keywords: CO2 laser; oral leukoplakia; oral squamous cell carcinoma; recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare any affiliation or significant financial involvement in any organizations or entity with a direct financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript on this page. This includes employment, honoraria, consultancies, or relevant stock ownership. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Different Laser-Supported Surgical Protocols for the Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia: A Long-Term Follow-Up.Photomed Laser Surg. 2017 Nov;35(11):629-638. doi: 10.1089/pho.2016.4256. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017. PMID: 28426376
-
Management of oral leukoplakia by laser surgery: relation between recurrence and malignant transformation and clinicopathological features.J Clin Laser Med Surg. 2004 Feb;22(1):27-33. doi: 10.1089/104454704773660949. J Clin Laser Med Surg. 2004. PMID: 15117484
-
Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia treated with carbon dioxide laser: a meta-analysis.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Feb;34(1):209-221. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2674-7. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30443884
-
The results of CO2 laser surgery in patients with oral leukoplakia: a 25 year follow up.Oral Oncol. 2005 Jan;41(1):31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2004.06.010. Oral Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15598583 Review.
-
Laser surgery as a treatment for oral leukoplakia.Oral Oncol. 2003 Dec;39(8):759-69. doi: 10.1016/s1368-8375(03)00043-5. Oral Oncol. 2003. PMID: 13679199 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrence in Oral Leukoplakia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Dent Res. 2024 Oct;103(11):1066-1075. doi: 10.1177/00220345241266519. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Dent Res. 2024. PMID: 39290142 Free PMC article.
-
Laser evaporation and excision of oral leukoplakia: Highlighting the two techniques for treating different risk lesions.J Dent Sci. 2024 Jul;19(3):1874-1876. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.03.001. Epub 2024 Mar 10. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39035316 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Is CO2 laser effective in the surgical management of oral potentially malignant disorders? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Mar 10;40(1):132. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04396-w. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40063178
-
Management of hormonal induced recurrent ulcerative fibrous epulis with osseous metaplasia: A case report.Clin Case Rep. 2023 Aug 25;11(9):e7828. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.7828. eCollection 2023 Sep. Clin Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37636873 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Laser in Minor Oral Surgery: A Systematic Review.J Lasers Med Sci. 2023 Oct 15;14:e44. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2023.44. eCollection 2023. J Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38028885 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Warnakulasuriya S., Kujan O., Aguirre-Urizar J.M., Bagan J.V., González-Moles M., Kerr A.R., Lodi G., Mello F.W., Monteiro L., Ogden G.R., et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A consensus report from an international seminar on nomenclature and classification, convened by the WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Cancer. Oral Dis. 2021;27:1862–1880. doi: 10.1111/odi.13704. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

