Replicative Instability Drives Cancer Progression
- PMID: 36358918
- PMCID: PMC9688014
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12111570
Replicative Instability Drives Cancer Progression
Abstract
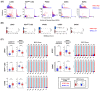
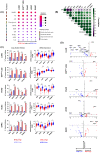
In the past decade, defective DNA repair has been increasingly linked with cancer progression. Human tumors with markers of defective DNA repair and increased replication stress exhibit genomic instability and poor survival rates across tumor types. Seminal studies have demonstrated that genomic instability develops following inactivation of BRCA1, BRCA2, or BRCA-related genes. However, it is recognized that many tumors exhibit genomic instability but lack BRCA inactivation. We sought to identify a pan-cancer mechanism that underpins genomic instability and cancer progression in BRCA-wildtype tumors. Methods: Using multi-omics data from two independent consortia, we analyzed data from dozens of tumor types to identify patient cohorts characterized by poor outcomes, genomic instability, and wildtype BRCA genes. We developed several novel metrics to identify the genetic underpinnings of genomic instability in tumors with wildtype BRCA. Associated clinical data was mined to analyze patient responses to standard of care therapies and potential differences in metastatic dissemination. Results: Systematic analysis of the DNA repair landscape revealed that defective single-strand break repair, translesion synthesis, and non-homologous end-joining effectors drive genomic instability in tumors with wildtype BRCA and BRCA-related genes. Importantly, we find that loss of these effectors promotes replication stress, therapy resistance, and increased primary carcinoma to brain metastasis. Conclusions: Our results have defined a new pan-cancer class of tumors characterized by replicative instability (RIN). RIN is defined by the accumulation of intra-chromosomal, gene-level gain and loss events at replication stress sensitive (RSS) genome sites. We find that RIN accelerates cancer progression by driving copy number alterations and transcriptional program rewiring that promote tumor evolution. Clinically, we find that RIN drives therapy resistance and distant metastases across multiple tumor types.
Keywords: MYBL2; cancer progression; metastasis; replicative instability (RIN); single-strand break repair; translesion synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
J.P.S., Q.Z., Z.J., O.A.H., M.L.C., A.S., S.M.A., W.L.A., M.A.V., P.T.S., A.R.P., H.C., V.F.B., J.M.L., A.C., J.L.V., E.A.S., P.M.D., C.B.M., C.M.U., and D.A.N. have no conflict of interest relevant to this study to disclose. B.B.M. and M.W.M. hold provisional patent Serial No. 63/252,007. K.H.S. has consultancy, advisor, and/or speaker roles with Adaptive Biotech, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda, Sanofi, Glaxo Smith Kline, and Amgen. He has research funding with Karyopharm and Abbvie, and funds from BMS and Janssen for clinical trials. DHO is supported in part by research funding from BMS, Merck, Genetech, Pfizer, Onc.AI, and Palobiofarma provided to OSUCC. DGS serves on the Novartis advisory board. HHS has consultancy roles with Novartis, Astrazeneca, Eisai, PUMA, Seattle Genetics, and Sanofi. He also is supported in part by research funding to Moffitt Cancer Center provided by Amgen. D.R.J. has a consultancy and advisory roles at AstraZeneca as well as a clinical trial steering committee role at Merck. R.D.G. has consultancy, advisor, and/or speaker roles with Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, BluePrint Medicines, Pfizer, Mirati, Sanofi, Oncocyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Rockepoint CME, Targeted Oncology, Total Health Conferencing, and OncLive. He is supported in part by research funding provided to UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center by Pfizer, Mirati, Daiichi Sankyo, Jounce Therapeutics, Helsinn, BMS, Merck, Janssen, and RTI International. D.G.S. has advisory roles for Novartis. J.E.G. has consultancy or advisory roles with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Axiom HC Strategies, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Celgene Copr, Diaachi Sankyo, EMD Serono, Genentech, Inivata, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Loxo Oncology, Merck, Norvartis, Sanofi, Takeda, OncoCyte, and Triptych Health Partners. She is supported in part by research funding provided by AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Genentech, G1 Therapeutics, Ludwig Institute of Cancer Research, Merck, Norvartis, and Pfizer. RGH has consultancy or advisory roles with BMS and Ono Pharmaceutical. He is supported in part by research funding to UVACC provided by Merck, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Mirati Therapeutics, Lilly, and Daiichi Sankyo.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

