LC-MS/MS Isomeric Profiling of N-Glycans Derived from Low-Abundant Serum Glycoproteins in Mild Cognitive Impairment Patients
- PMID: 36359007
- PMCID: PMC9687829
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12111657
LC-MS/MS Isomeric Profiling of N-Glycans Derived from Low-Abundant Serum Glycoproteins in Mild Cognitive Impairment Patients
Abstract
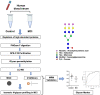
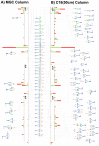
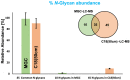
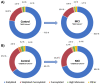
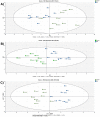
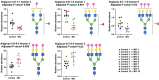
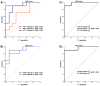
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is an early stage of memory loss that affects cognitive abilities, such as language or virtual/spatial comprehension. This cognitive decline is mostly observed with the aging of individuals. Recently, MCI has been considered as a prodromal phase of Alzheimer's disease (AD), with a 10-15% conversion rate. However, the existing diagnostic methods fail to provide precise and well-timed diagnoses, and the pathophysiology of MCI is not fully understood. Alterations of serum N-glycan expression could represent essential contributors to the overall pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases and be used as a potential marker to assess MCI diagnosis using non-invasive procedures. Herein, we undertook an LC-MS/MS glycomics approach to determine and characterize potential N-glycan markers in depleted blood serum samples from MCI patients. For the first time, we profiled the isomeric glycome of the low abundant serum glycoproteins extracted from serum samples of control and MCI patients using an LC-MS/MS analytical strategy. Additionally, the MRM validation of the identified data showed five isomeric N-glycans with the ability to discriminate between healthy and MCI patients: the sialylated N-glycans GlcNAc5,Hex6,Neu5Ac3 and GlcNAc6,Hex7,Neu5Ac4 with single AUCs of 0.92 and 0.87, respectively, and a combined AUC of 0.96; and the sialylated-fucosylated N-glycans GlcNAc4,Hex5,Fuc,Neu5Ac, GlcNAc5,Hex6,Fuc,Neu5Ac2, and GlcNAc6,Hex7,Fuc,Neu5Ac3 with single AUCs of 0.94, 0.67, and 0.88, respectively, and a combined AUC of 0.98. According to the ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) and in line with recent publications, the identified N-glycans may play an important role in neuroinflammation. It is a process that plays a fundamental role in neuroinflammation, an important process in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: MCI; biomarker glycan; isomeric N-glycans; neurological disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of N-glycopeptides derived from serum glycoproteins in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients.Proteomics. 2024 Oct;24(20):e2300620. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202300620. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38602241
-
LC-MS/MS glycomics of idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder.Electrophoresis. 2018 Dec;39(24):3096-3103. doi: 10.1002/elps.201800316. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Electrophoresis. 2018. PMID: 30168606 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS isomeric profiling of permethylated N-glycans derived from serum haptoglobin of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cirrhotic patients.Electrophoresis. 2017 Sep;38(17):2160-2167. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700025. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28543513 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitation of permethylated N-glycans through multiple-reaction monitoring (MRM) LC-MS/MS.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015 Apr;26(4):596-603. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-1054-1. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 25698222 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of isomeric glycan structures by LC-MS/MS.Electrophoresis. 2017 Sep;38(17):2100-2114. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700042. Epub 2017 May 17. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28370073 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppressing the background of LC-ESI-MS analysis of permethylated glycans using the active background ion reduction device.Electrophoresis. 2024 Sep;45(17-18):1469-1478. doi: 10.1002/elps.202300301. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Electrophoresis. 2024. PMID: 38573014
-
Differential expression of N-glycopeptides derived from serum glycoproteins in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients.Proteomics. 2024 Oct;24(20):e2300620. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202300620. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38602241
-
Serum N-Glycan Changes in Rats Chronically Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicides.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 28;14(9):1077. doi: 10.3390/biom14091077. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334844 Free PMC article.
-
Serum N-Glycan Profiling of Patients with Narcolepsy Type 1 Using LC-MS/MS.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 16;9(30):32628-32638. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01593. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39100283 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS Quantitation of HILIC-Enriched N-glycopeptides Derived from Low-Abundance Serum Glycoproteins in Patients with Narcolepsy Type 1.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 28;13(11):1589. doi: 10.3390/biom13111589. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Solfrizzi V., Panza F., Colacicco A.M., D’Introno A., Capurso C., Torres F., Grigoletto F., Maggi S., Del Parigi A., Reiman E.M., et al. Vascular risk factors, incidence of MCI, and rates of progression to dementia. Neurology. 2004;63:1882–1891. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000144281.38555.E3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

