The Role of NF-κB and Bax/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways in the Protective Effects of Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) against HFD/STZ-Induced Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 36359384
- PMCID: PMC9717728
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10112863
The Role of NF-κB and Bax/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways in the Protective Effects of Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) against HFD/STZ-Induced Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
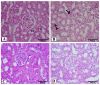
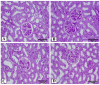
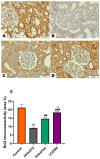
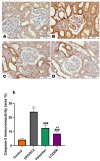
LCZ696 (valsartan/sacubitril) has the potential to slow the progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) according to previous reports. However, the renoprotective mechanism underlying LCZ696 remains unknown. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic potential and underlying mechanism of LCZ696 in DKD in a type 2 diabetic (T2D) rat model. This model was established in this experiment by feeding a high-fat diet (HFD) for six weeks with a single dose of streptozotocin (STZ, 30 mg/kg body weight). Valsartan or LCZ696 was orally administered to T2D animals for eight weeks. HFD/STZ rats showed hyperglycemia, impaired insulin secretion, significant increases in urea, creatinine, cytokines, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), oxidative stress, caspase-3 activity, glomerular and tubular damage, glomerulsclerosis, Bax and caspese-3 expressions along with a significant decline in IL-10, antioxidant markers, and Bcl-2 expression. The administration of LCZ696 to diabetic rats reduced the serum concentrations of glucose, urea, and creatinine. In addition, ELISA results demonstrated that diabetic rats treated with LCZ696 exhibited a reduction in inflammatory (IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6) and an increase in anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokine levels. In addition, a notable decrease in NF-κB and caspase-3 activity was observed. At the level of renal tissue homogenate, diabetic animals treated with LCZ696 demonstrated clear restorations in GSH content and other antioxidant enzyme levels, in addition to a significant decrease in TBARS levels. In addition, LCZ696 inhibited the expression of the Bax and cleaved caspase-3 proteins and enhanced the expression of the Bcl-2 protein. Improvements in histopathological changes in kidney tissues confirmed and significantly supported these biochemical findings. In summary, LCZ696 alleviated DKD with possible mechanisms including inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis.
Keywords: LCZ696; apoptotic markers; diabetic kidney disease; inflammation; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II receptor Neprilysin inhibitor (LCZ696) compared to Valsartan attenuates Hepatotoxicity in STZ-induced hyperglycemic rats.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Oct 22;17(18):3098-3106. doi: 10.7150/ijms.49373. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33173431 Free PMC article.
-
LCZ696 mitigates diabetic-induced nephropathy through inhibiting oxidative stress, NF-κB mediated inflammation and glomerulosclerosis in rats.PeerJ. 2020 Jun 19;8:e9196. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9196. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32596035 Free PMC article.
-
LCZ696 Protects against Diabetic Cardiomyopathy-Induced Myocardial Inflammation, ER Stress, and Apoptosis through Inhibiting AGEs/NF-κB and PERK/CHOP Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 24;23(3):1288. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031288. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163209 Free PMC article.
-
LCZ696 (sacubitril/valsartan) mitigates cyclophosphamide-induced premature ovarian failure in rats; the role of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2023 Aug 1;326:121789. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121789. Epub 2023 May 17. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37201697
-
Abietic acid ameliorates nephropathy progression via mitigating renal oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis in high fat diet and low dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Phytomedicine. 2022 Dec;107:154464. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154464. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36215789
Cited by
-
Ameliorative impact of sacubitril/valsartan on paraquat-induced acute lung injury: role of Nrf2 and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8785-8796. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03785-w. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39869189 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating cerebral neurovascular responses to hyperglycemia in a rat model of type 2 diabetes using multimodal assessment techniques.iScience. 2024 May 24;27(6):110108. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110108. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38952685 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin alone and in combination with metformin mitigates diabetes-associated renal complications.J Med Life. 2024 May;17(5):530-535. doi: 10.25122/jml-2023-0301. J Med Life. 2024. PMID: 39144694 Free PMC article.
-
Rosmarinic acid attenuated inflammation and apoptosis in folic acid-induced renal injury: Role of FoxO3/ NFκB pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(3):316-322. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.80551.17436. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39906624 Free PMC article.
-
Sacubitril/valsartan ameliorates tubulointerstitial fibrosis by restoring mitochondrial homeostasis in diabetic kidney disease.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Feb 10;16(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01284-1. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38341600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhatti J.S., Sehrawat A., Mishra J., Sidhu I.S., Navik U., Khullar N., Kumar S., Bhatti G.K., Reddy P.H. Oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and related complications: Current therapeutics strategies and future perspectives. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022;184:114–134. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.03.019. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

