Functionalized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody
- PMID: 36359457
- PMCID: PMC9689474
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12112612
Functionalized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody
Abstract
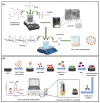
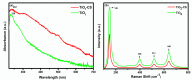
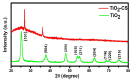
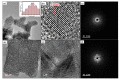
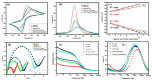
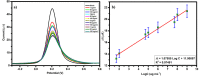
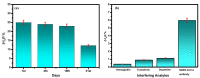
The advancement in biosensors can overcome the challenges faced by conventional diagnostic techniques for the detection of the highly infectious severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Hence, the development of an accurate, rapid, sensitive, and selective diagnostic technique can mitigate adverse health conditions caused by SARS-CoV-2. This work proposes the development of an electrochemical immunosensor based on bio-nanocomposites for the sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies through the differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) electroanalytical method. The facile synthesis of chitosan-functionalized titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2-CS bio-nanocomposites) is performed using the sol-gel method. Characterization of the TiO2-CS bio-nanocomposite is accomplished using UV-vis spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The electrochemical performance is studied using cyclic voltammetry (CV), DPV, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for its electroanalytical and biosensing capabilities. The developed immunosensing platform has a high sensitivity with a wide range of detection from 50 ag mL-1 to 1 ng mL-1. The detection limit of the SARS-CoV-2 antibody in buffer media is obtained to be 3.42 ag mL-1 and the limit of quantitation (LOQ) to be 10.38 ag mL-1. The electrochemical immunosensor has high selectivity in different interfering analytes and is stable for 10 days. The results suggest that the developed electrochemical immunosensor can be applicable for real sample analysis and further high-throughput testing.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 N protein; SARS-CoV-2 antibody; chitosan; electrochemical immunosensor; titanium dioxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor Platforms for Dual Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen and Antibody based on Gold Nanoparticle Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022 May 16;5(5):2421-2430. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00301. Epub 2022 May 6. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022. PMID: 35522141
-
Polydopamine decorated MoS2 nanosheet based electrochemical immunosensor for sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in clinical samples.J Mater Chem B. 2022 Oct 26;10(41):8478-8489. doi: 10.1039/d2tb01409b. J Mater Chem B. 2022. PMID: 36197135
-
Electrochemical immunosensor nanoarchitectonics with the Ag-rGO nanocomposites for the detection of receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.J Solid State Electrochem. 2023;27(2):489-499. doi: 10.1007/s10008-022-05330-8. Epub 2022 Nov 29. J Solid State Electrochem. 2023. PMID: 36466035 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Immunosensor for Early Detection of β-Amyloid Alzheimer's Disease Biomarker Based on Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Gold Nanocomposites.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;12(11):1059. doi: 10.3390/bios12111059. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421177 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 pathogen and protein biomarkers.Int J Electrochem Sci. 2022 May;17(5):220541. doi: 10.20964/2022.05.13. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 37360860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polyaniline/Titania Nanotube-Based Biosensor Strip for Sensitive and Specific Electrochemical Detection of SARS-CoV-2.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 22;8(48):45700-45707. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c06133. eCollection 2023 Dec 5. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38075789 Free PMC article.
-
Internet-of-medical-things integrated point-of-care biosensing devices for infectious diseases: Toward better preparedness for futuristic pandemics.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 Jan 3;8(3):e10481. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10481. eCollection 2023 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37206204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanostructured Metal Oxide-Based Electrochemical Biosensors in Medical Diagnosis.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 May 9;14(5):238. doi: 10.3390/bios14050238. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38785712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Point-of-Care Diagnostic Biosensors to Monitor Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing IgG/sIgA Antibodies and Antioxidant Activity in Saliva.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;13(2):167. doi: 10.3390/bios13020167. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831933 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosensors for Assay of Toxic Biological Warfare Agents.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 20;13(3):402. doi: 10.3390/bios13030402. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

